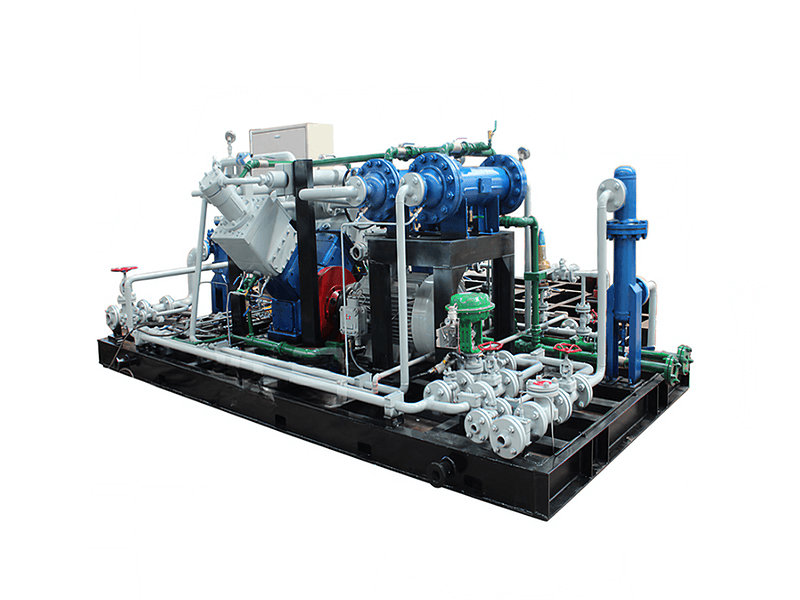
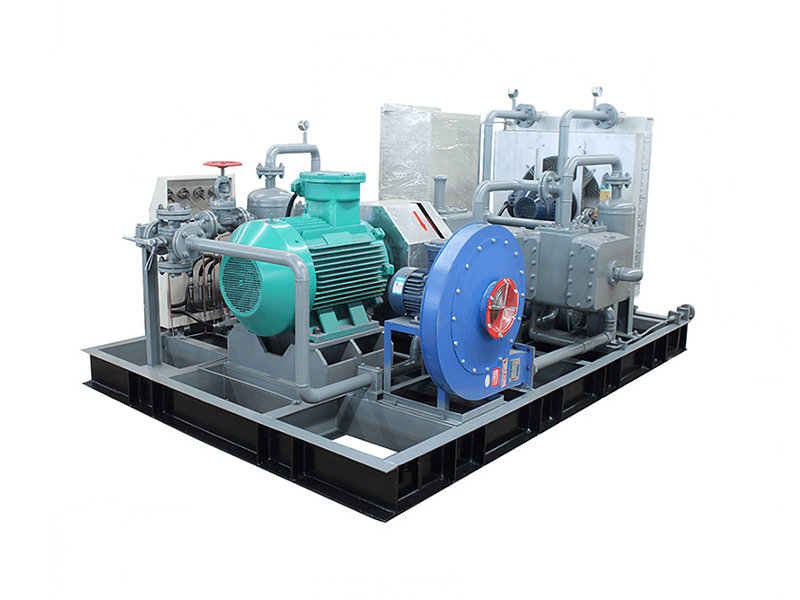
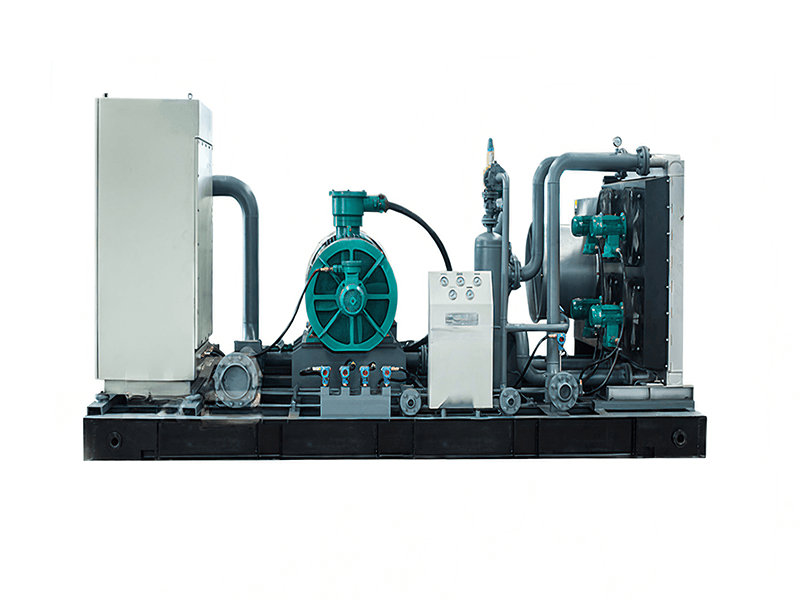
A CNG (Compressed Natural Gas) standard station, also known as a CNG fueling station, is a facility designed to dispense compressed natural gas as a vehicle fuel. These stations provide a convenient and accessible location for CNG-powered vehicles to refuel.
Key features and components typically found in a CNG standard station:
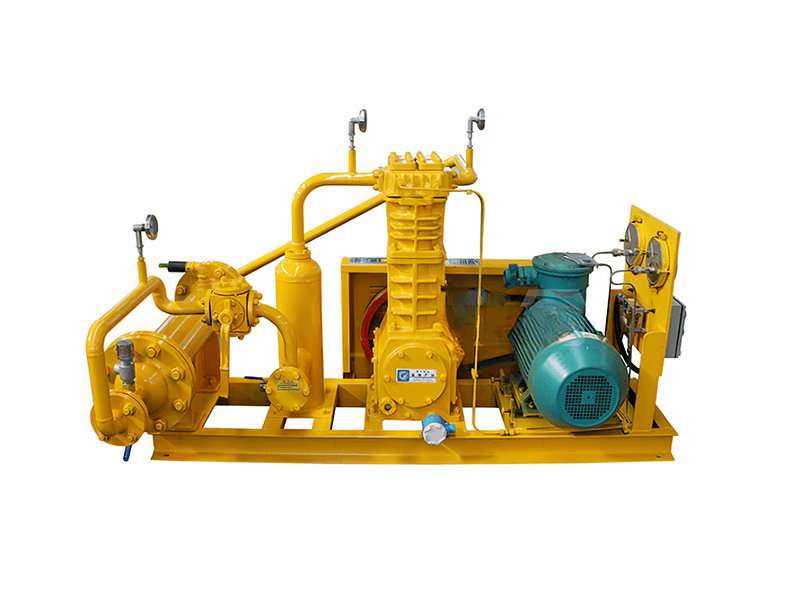
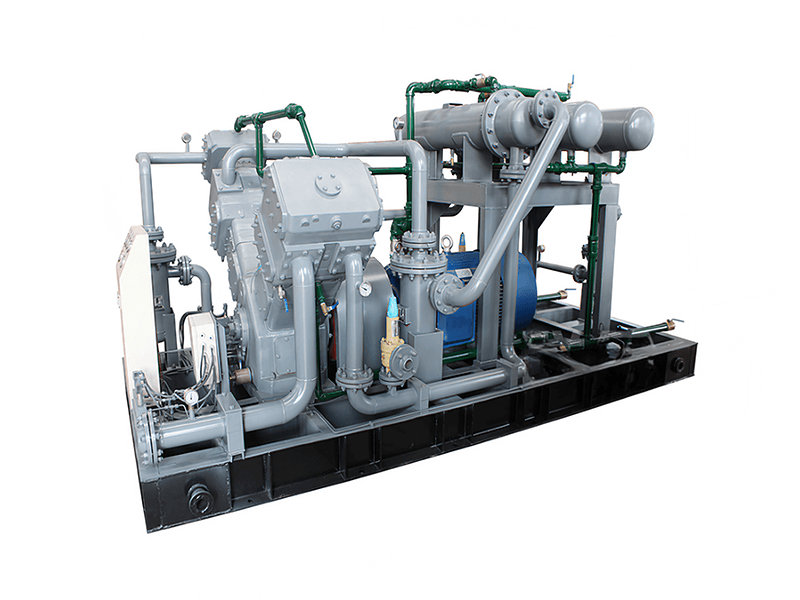
1. Compressor System:
- The compressor system is the heart of a CNG station. It compresses natural gas from the utility pipeline or storage tanks to high pressures, typically ranging from 3,000 to 3,600 pounds per square inch (psi), or even higher for certain applications.
- The compressor system includes several stages of compression to achieve the desired pressure, and it is designed to handle the required flow rates to meet the refueling demand.
2. Storage System:
- A CNG station typically includes storage vessels or cylinders to store the compressed natural gas. These storage systems can be above-ground or underground, and they store the gas at high pressures until it is dispensed into the vehicles.
- Storage capacities vary depending on the station's size and expected refueling demand, ranging from a few hundred to thousands of cubic feet of gas.
3. Dispensing Equipment:
- The dispensing equipment comprises hoses, nozzles, and safety features necessary for safely transferring CNG from the storage system to the vehicles.
- Safety features include breakaway connectors, emergency shut-off valves, and pressure relief devices to prevent accidents and ensure safe operation.
4. Control and Monitoring Systems:
- CNG stations incorporate control and monitoring systems to regulate the flow of gas, manage the compressor operation, and ensure proper pressure control during refueling.
- These systems include sensors, valves, regulators, and automation controls that monitor and maintain the required pressure and safety parameters.
5. Safety Systems:
- CNG stations prioritize safety and are equipped with various safety systems to prevent accidents and respond to emergencies. This includes fire suppression systems, gas leak detection systems, emergency shutdown systems, and proper ventilation to handle any potential gas leaks.
6. Filtration and Drying:
- Natural gas extracted from pipelines may contain impurities such as moisture, oil, and solid particles. CNG stations incorporate filtration and drying systems to remove these impurities and ensure the quality of the dispensed gas.
7. Communication and Payment Systems:
- CNG stations often include systems for communication and payment, allowing users to authorize and pay for their fueling transactions. This may involve fueling cards, RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) systems, or other electronic payment methods.
8. Station Siting and Design:
- The siting and design of CNG standard stations are crucial considerations. Stations are strategically located to ensure accessibility for CNG vehicles, considering factors such as proximity to major transportation routes, fleet operations, and population centers.
- The station layout is designed to accommodate the flow of vehicles, ensuring efficient circulation and safe maneuvering during fueling operations.
9. Fast-fill and Time-fill Systems:
- CNG standard stations can be designed as either fast-fill or time-fill systems, depending on the refueling requirements and the types of vehicles served.
- Fast-fill systems dispense CNG quickly, similar to conventional gasoline or diesel fueling, allowing vehicles to refuel in a matter of minutes.
- Time-fill systems are typically used for fleets of vehicles that can be parked for an extended period, such as overnight. These systems dispense CNG at a slower rate over a longer period, often using multiple fueling hoses simultaneously.
10. Maintenance and Service:
- Regular maintenance and service are essential for the continued safe and reliable operation of CNG standard stations.
- Station operators follow maintenance schedules and perform routine inspections to ensure equipment integrity, detect any potential leaks or malfunctions, and address any issues promptly.
- Qualified technicians, trained in CNG station maintenance and safety procedures, perform maintenance tasks and respond to service calls as needed.
11. Safety Training and Procedures:
- CNG station operators prioritize safety and provide training to employees regarding the proper handling of CNG, emergency response procedures, and safety protocols.
- Employees are trained to identify potential hazards, manage emergency situations, and follow safety guidelines to mitigate risks associated with CNG handling and fueling operations.
12. Regulatory Compliance:
- CNG standard stations must comply with applicable regulations and codes related to safety, environmental protection, and quality standards.
- These regulations may include adherence to specific design criteria, proper operation and maintenance procedures, safety inspections, and compliance with local, state, and national guidelines.
It's important to note that CNG standard stations are part of a broader infrastructure network that supports the use of CNG as a transportation fuel. They work in conjunction with natural gas production, compression, and distribution systems to ensure a reliable supply of CNG for vehicles across different regions. As the demand for clean and sustainable transportation options continues to grow, the development of CNG standard stations remains an important aspect of promoting the use of natural gas as a fuel source.