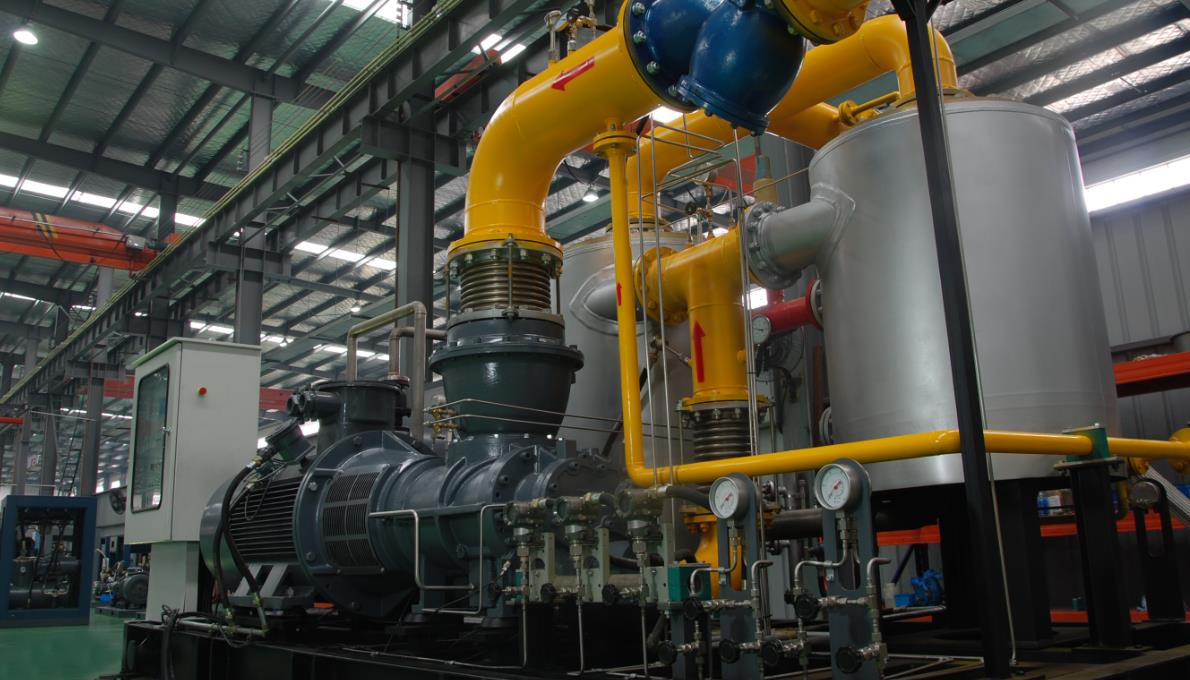
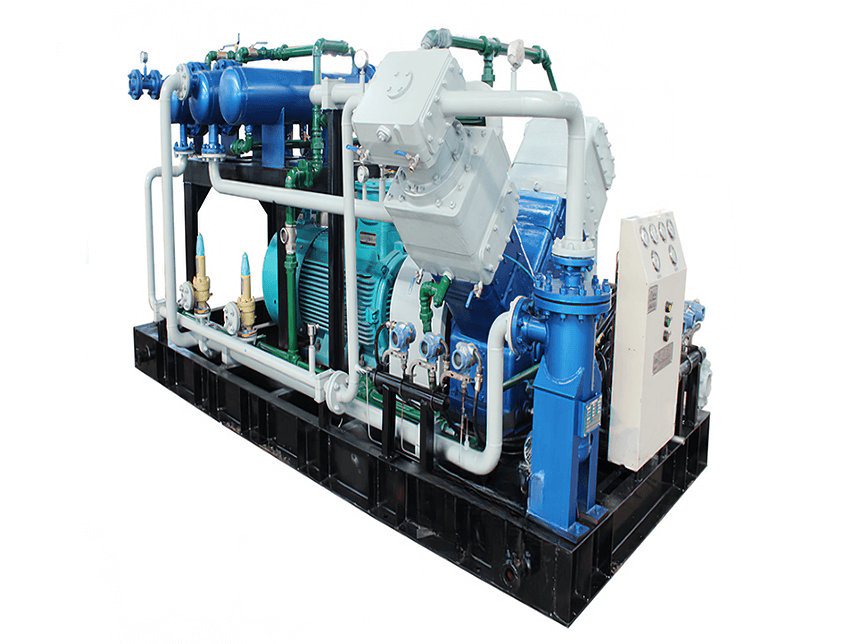
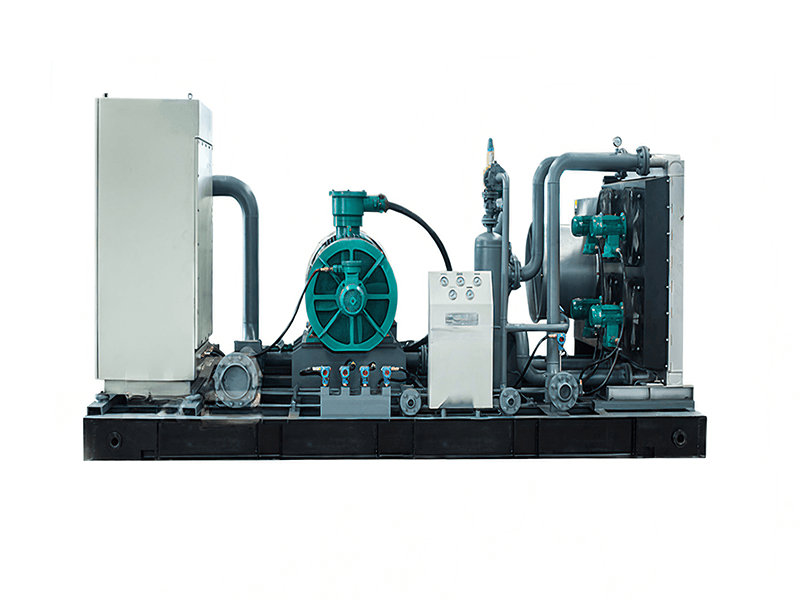
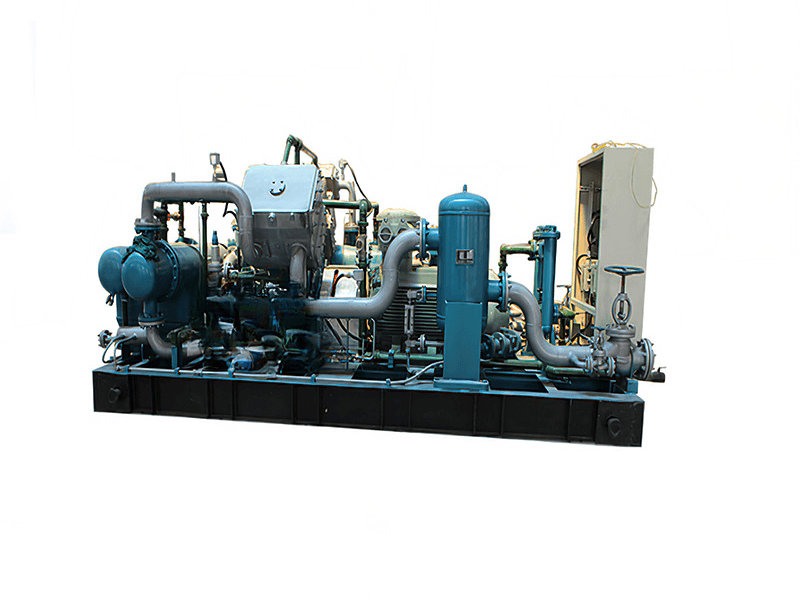
When considering nitrogen compressors for industrial nitrogen compression, several requirements need to be taken into account to ensure proper performance and efficiency. Here are some key requirements to consider:
1. Flow Rate: Determine the required flow rate of compressed nitrogen based on the specific application and usage. The flow rate is typically measured in standard cubic feet per minute (SCFM) or cubic meters per hour (m³/h).
2. Pressure Range: Determine the required discharge pressure range for the compressed nitrogen. Different applications may have varying pressure requirements, so it's essential to select a compressor capable of delivering the desired pressure range.
3. Gas Purity: Consider the required purity level of the compressed nitrogen. Some applications may require high-purity nitrogen, necessitating additional filtration or purification systems in conjunction with the compressor.
4. Compressor Type: Select the appropriate compressor type based on the application requirements. Common types of compressors used for nitrogen compression include reciprocating compressors, rotary screw compressors, and centrifugal compressors. Each type has its advantages and limitations, so choose one that suits the specific needs of the application.
5. Materials of Construction: Nitrogen compressors should be constructed using materials compatible with nitrogen gas, ensuring corrosion resistance and longevity. Consider the compatibility of materials with the nitrogen gas and any other gases or contaminants present in the system.
6. Cooling and Lubrication: Nitrogen compression generates heat, so proper cooling systems such as intercoolers or aftercoolers should be incorporated to maintain optimal operating temperatures. Lubrication systems should also be considered to ensure smooth operation and reduce wear on compressor components.

7. Safety Features: Nitrogen compressors should incorporate necessary safety features, such as pressure relief valves, temperature sensors, and shutdown controls, to ensure safe operation and protect against overpressure or overheating situations.
8. Energy Efficiency: Consider the energy efficiency of the compressor to optimize power consumption and operating costs. Look for compressors with energy-saving features like variable speed drives or efficient control systems.
9. Maintenance and Serviceability: Assess the ease of maintenance, availability of spare parts, and service support provided by the compressor manufacturer. Regular maintenance and timely service are crucial to ensure the longevity and reliable performance of the nitrogen compressor.
10. Compliance with Standards: Ensure that the nitrogen compressor meets relevant industry standards and regulations, such as those related to safety, performance, and environmental considerations.
It's essential to consult with compressor manufacturers, system designers, or experts in nitrogen compression to determine the specific requirements and select the most suitable nitrogen compressor for your industrial application.
Characteristics of different types of nitrogen compressors
Different types of nitrogen compressors possess unique characteristics that make them suitable for various applications. Here are the characteristics of three common types of nitrogen compressors:
1. Reciprocating Compressors:
- Operating Principle: Reciprocating compressors use a piston-cylinder arrangement to compress gases. The piston moves back and forth within the cylinder, creating compression during the forward stroke.
- Pressure Range: Reciprocating compressors can achieve high-pressure ranges, making them suitable for applications requiring high-pressure nitrogen.
- Flow Control: Reciprocating compressors offer good flow control, allowing for modulation and adjustment of the discharge flow rate.
- Efficiency: Reciprocating compressors can provide high efficiency, especially in small to medium-sized applications. They offer good compression ratios and are well-suited for intermittent or variable load conditions.
- Maintenance: Reciprocating compressors generally require more maintenance due to the complexity of the piston-cylinder arrangement. Regular inspections and maintenance of valves, rings, and lubrication systems are necessary.
2. Rotary Screw Compressors:
- Operating Principle: Rotary screw compressors use two interlocking helical screws to compress gases. As the screws rotate, the gas is trapped and compressed between the screws and the housing.
- Pressure Range: Rotary screw compressors can deliver moderate to high-pressure ranges, making them suitable for a wide range of nitrogen compression applications.
- Continuous Operation: Rotary screw compressors excel in continuous duty applications, where a constant supply of compressed nitrogen is required.
- Efficiency: Rotary screw compressors offer good efficiency with relatively high compression ratios. They are known for their smooth and continuous operation.
- Maintenance: Rotary screw compressors generally require less maintenance compared to reciprocating compressors. Routine maintenance includes filter replacements, oil changes, and periodic inspections.
3. Centrifugal Compressors:
- Operating Principle: Centrifugal compressors use a rotating impeller to accelerate nitrogen gas, converting kinetic energy into potential energy, which results in compression.
- Pressure Range: Centrifugal compressors are well-suited for high-pressure applications and can handle a wide range of pressure requirements.
- Large Flow Rates: Centrifugal compressors excel in delivering large flow rates of compressed nitrogen, making them suitable for high-volume applications.
- Efficiency: Centrifugal compressors offer excellent efficiency in continuous operation, particularly in applications with high flow rates and moderate pressure ratios.
- Maintenance: Centrifugal compressors typically require regular maintenance of bearings, seals, and lubrication systems. Their maintenance requirements can vary based on the specific design and configuration.
It's important to note that the specific performance and characteristics of nitrogen compressors can vary among different manufacturers and models. When selecting a compressor, it's essential to consider the specific requirements of the application, such as flow rate, pressure range, efficiency, and maintenance considerations, to choose the most suitable compressor type. Consulting with compressor manufacturers or experts in the field can provide additional guidance in selecting the appropriate nitrogen compressor for your specific needs.