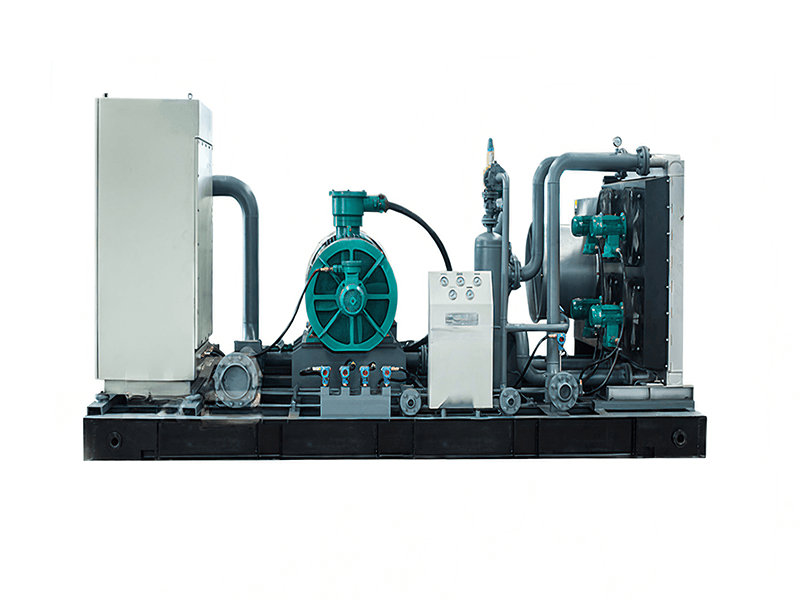
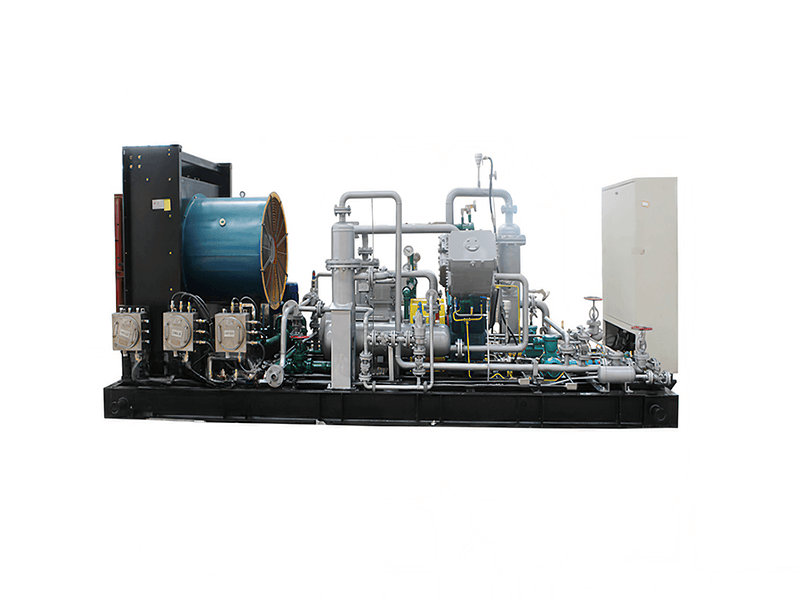
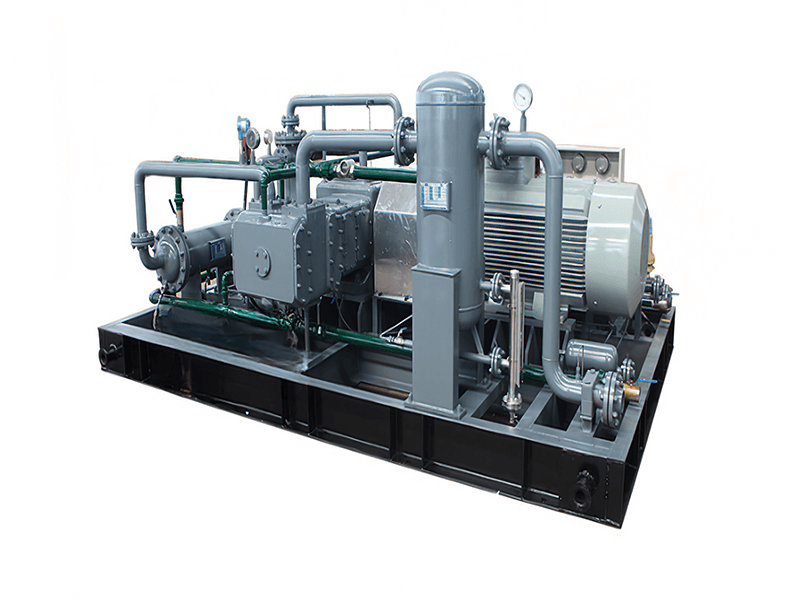
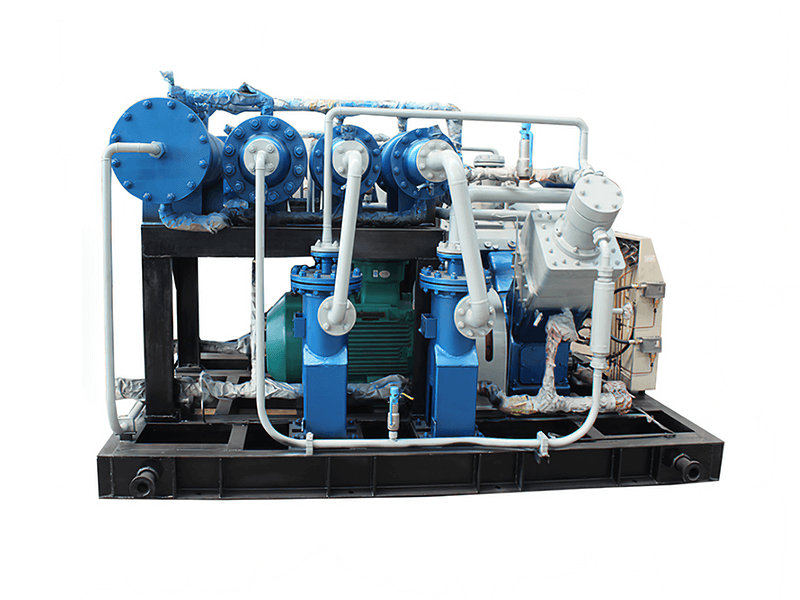
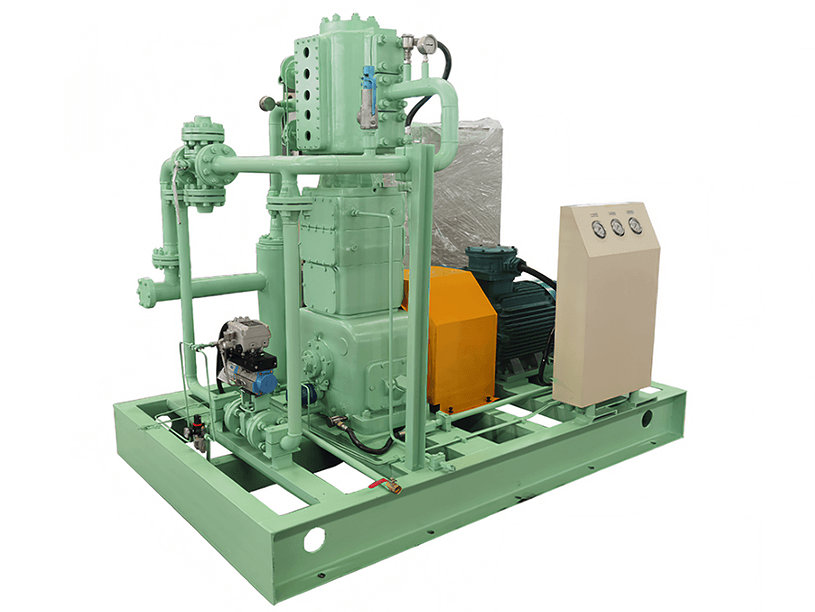
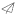
A CNG standard station compressor typically consists of several components that work together to compress natural gas for refueling CNG vehicles. Here are the main components of a CNG standard station compressor:
1. Compressor Unit: The core component of the system is the compressor unit itself. It is responsible for taking in natural gas at a lower pressure and compressing it to the desired high-pressure level for vehicle refueling. The compressor unit may consist of multiple stages or cylinders to achieve the required compression ratio.
2. Electric Motor or Engine: The compressor unit is driven by an electric motor or an internal combustion engine (typically natural gas-powered) that provides the mechanical power required for the compression process. The motor or engine converts electrical or chemical energy into mechanical energy to drive the compressor.
3. Cooling System: Compressing natural gas generates heat, so a cooling system is crucial to maintain optimal operating temperatures. The cooling system may include air cooling or water cooling mechanisms to dissipate the heat produced during compression and prevent overheating of the compressor.

4. Lubrication System: Compressor components require proper lubrication to reduce friction and wear. A lubrication system is employed to ensure that the moving parts of the compressor, such as pistons and cylinders, are adequately lubricated, enhancing their longevity and performance.
5. Intake Filtration: Natural gas entering the compressor must be filtered to remove impurities and contaminants that may damage the compressor components. Intake filters capture particles, moisture, and other unwanted substances present in the gas stream, protecting the compressor from potential damage.
6. Pressure Regulation and Control: The compressor system incorporates pressure regulation and control mechanisms to maintain the desired pressure levels during compression and ensure safe and efficient operation. Pressure sensors and valves are utilized to monitor and adjust the gas pressure at various stages of the compression process.
7. Safety Features: CNG standard station compressors incorporate safety features to protect against potential hazards. These can include pressure relief valves, emergency shut-off systems, and temperature sensors that detect abnormal operating conditions and trigger safety measures to prevent accidents or equipment damage.
8. Control and Monitoring Systems: Compressor operations are often controlled and monitored using specialized systems. These systems regulate the compressor's performance, monitor critical parameters such as pressure, temperature, and flow rates, and provide real-time feedback on the compressor's status.
9. Maintenance and Serviceability: Compressor units are designed with maintenance and serviceability in mind. They often have accessible components, such as filters, valves, and lubrication points, that can be easily inspected, maintained, or replaced. Manufacturers may provide guidelines for routine maintenance and offer support for servicing the compressors.
These are the typical components found in a CNG standard station compressor. The specific design and configuration may vary depending on the manufacturer, model, and capacity of the compressor, as well as the requirements of the CNG station.
Maintenance of CNG Standard Station Compressor
Proper maintenance of a CNG standard station compressor is crucial to ensure its reliable and efficient operation. Regular maintenance helps prevent breakdowns, extends the lifespan of the equipment, and promotes the safety of the compressor system. Here are some key aspects of maintaining a CNG standard station compressor:
1. Follow Manufacturer Guidelines: Start by familiarizing yourself with the manufacturer's maintenance guidelines and recommendations specific to your compressor model. The manufacturer's guidelines will provide detailed instructions on maintenance intervals, procedures, and any specific considerations for your particular compressor.
2. Routine Inspections: Conduct regular visual inspections of the compressor system to identify any signs of wear, leaks, or damage. Inspect components such as belts, hoses, valves, and fittings for any signs of degradation or malfunction.
3. Lubrication: Follow the manufacturer's recommendations for lubrication. Ensure that the compressor's lubrication system is functioning correctly and that the appropriate lubricants are being used. Regularly check oil levels and change the lubricant as per the recommended schedule.
4. Filter Maintenance: Clean or replace intake filters regularly to prevent contaminants from entering the compressor system. Dirty or clogged filters can reduce efficiency and potentially damage the compressor components. Follow the manufacturer's guidelines for filter maintenance intervals and replacement.
5. Cooling System Maintenance: Monitor and maintain the cooling system of the compressor. Clean or replace air filters or clean cooling fins regularly to ensure proper airflow and prevent overheating. Check coolant levels, inspect hoses, and address any cooling system leaks promptly.
6. Pressure Relief Valve Testing: Test and inspect pressure relief valves periodically to ensure they are functioning correctly. Pressure relief valves are safety devices that protect the compressor from excessive pressure build-up. They should be tested according to the manufacturer's recommendations.
7. Electrical System Maintenance: If the compressor is powered by an electric motor, inspect and maintain the electrical components regularly. Check for loose connections, damaged wiring, or signs of electrical issues. Follow proper electrical safety protocols when working on electrical components.
8. Maintain Service Records: Keep detailed records of all maintenance activities, including inspections, lubrication, filter changes, and repairs. These records can help track the maintenance history of the compressor, identify recurring issues, and ensure that maintenance tasks are performed on schedule.
9. Training and Qualified Personnel: Ensure that maintenance tasks are performed by qualified personnel who have the necessary training and experience in working with CNG compressors. This helps ensure that maintenance procedures are conducted safely and effectively.
10. Professional Service and Support: Engage with authorized service providers or manufacturers for any major repairs, complex maintenance tasks, or when encountering technical issues beyond the scope of routine maintenance. Professional service technicians can offer expert assistance and ensure that the compressor is properly serviced.
Remember that maintenance requirements may vary depending on the specific compressor model, operating conditions, and manufacturer guidelines. It is important to consult the manufacturer's documentation and seek professional advice when needed to ensure the proper maintenance of your CNG standard station compressor.