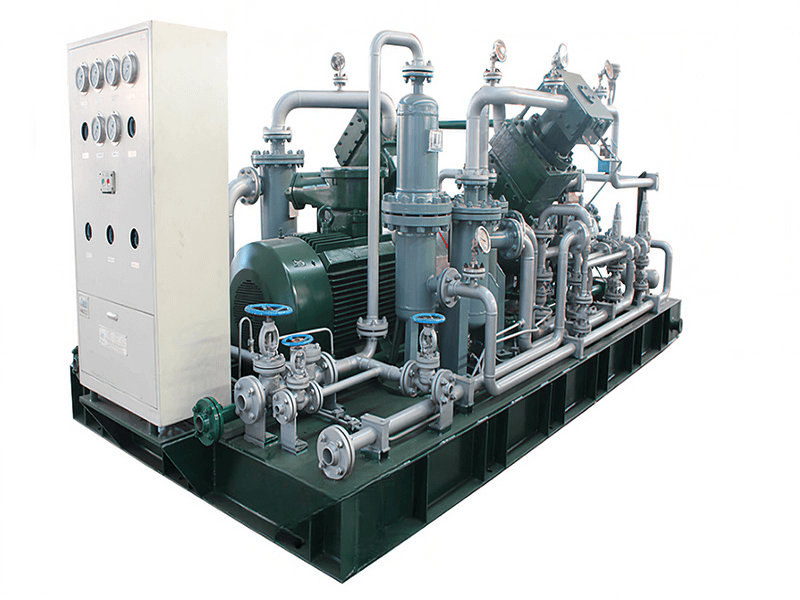
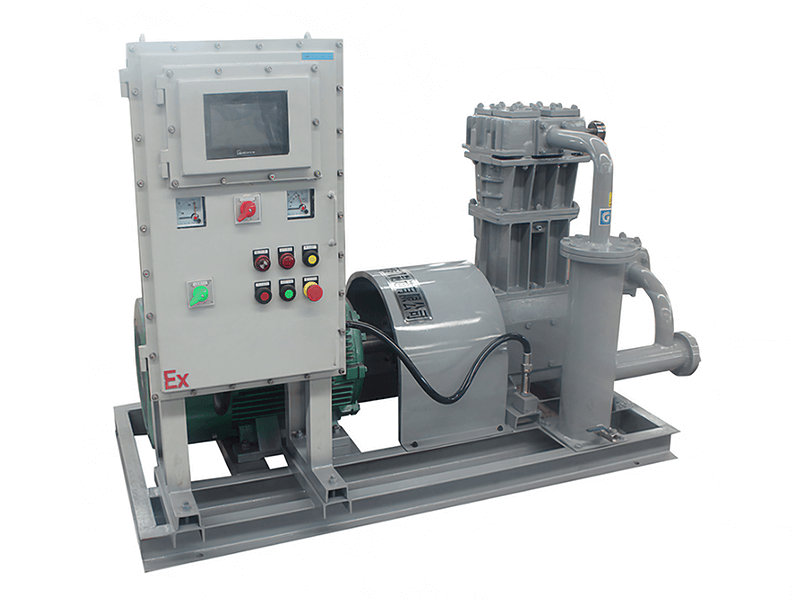
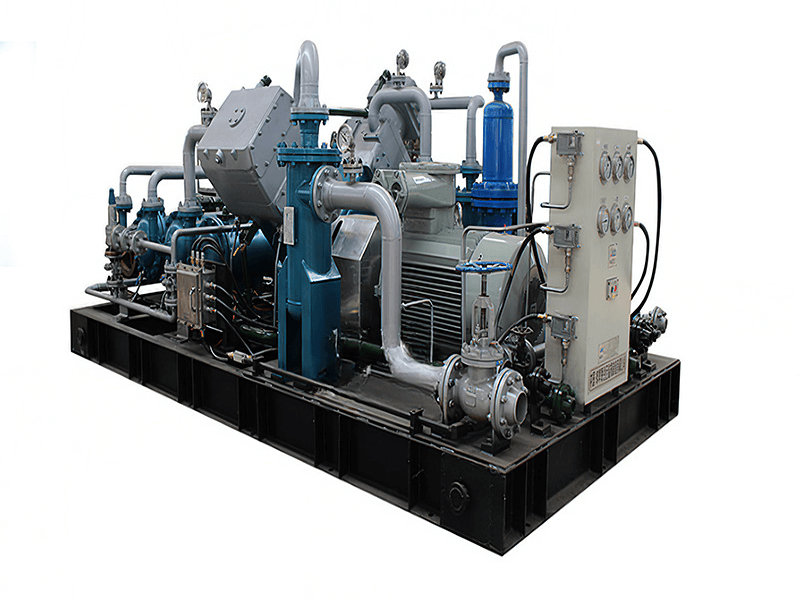
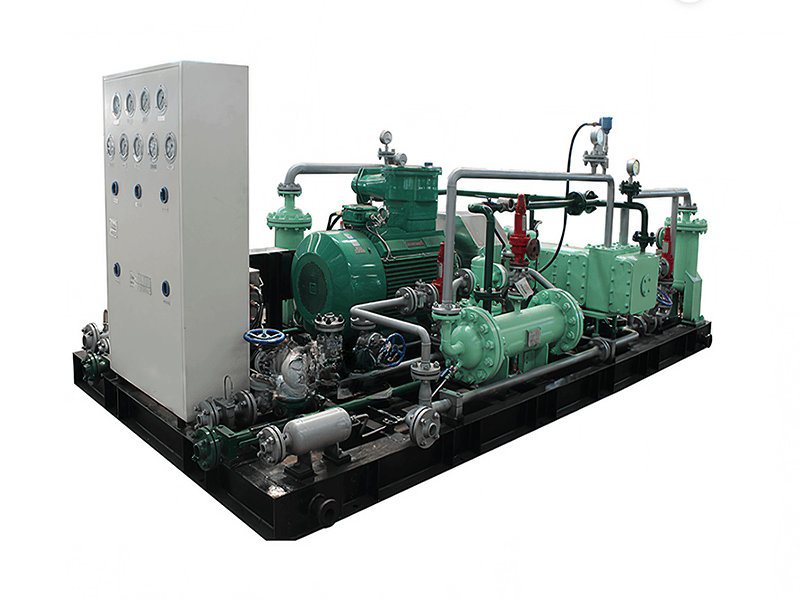
【不见星空汉服完整播放】最新入口
-

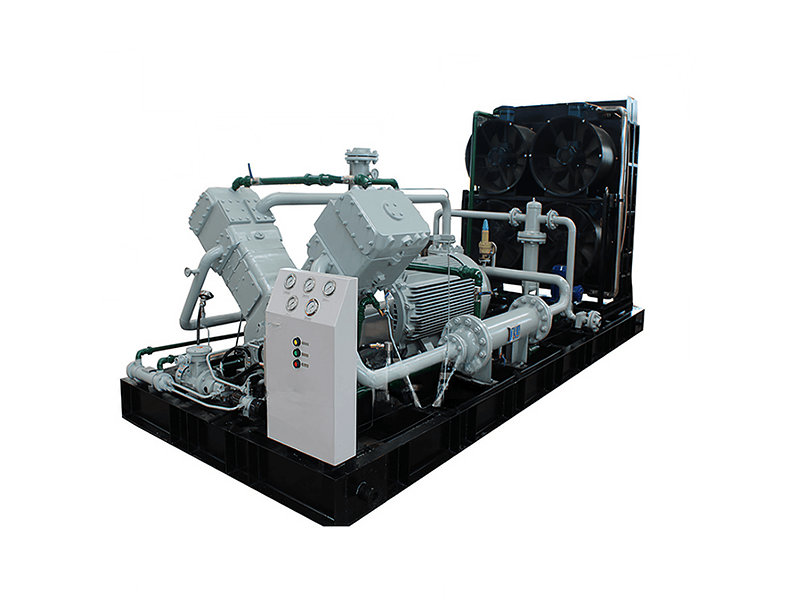
Requirements for hydrogen compression for hydrogen compressors
Jul 15, 2024 -

Applications of butadiene compression and butadiene compressor
Jun 19, 2024 -

Characteristics of hydrogen compressors in different industries
Jun 24, 2024 -

Main components and maintenance of a CNG standard station compressor
May 31, 2024 -

Requirements for Nitrogen Compressors in Industrial Nitrogen Compression
Jul 18, 2024 -

Rich gas and rich gas recovery
Jun 01, 2024
不见星空汉服完整播放【乾坤易变】Jun 09, 2024
by:Anhui Shengnuo Compressor Manufacturing Co.,Ltd
Follow Us:
Choosing the appropriate parameters for a mixed gas compressor involves considering several factors to ensure optimal performance and efficiency. Here are some key steps to guide you in selecting the right parameters:
1. Understand Gas Composition: Start by understanding the composition of the mixed gas you need to compress. Determine the individual gas components, their concentrations, and any potential impurities. This information is crucial for selecting a compressor that can handle the specific gas mixture and any associated challenges.
2. Determine Compression Ratio: The compression ratio is the ratio of the discharge pressure to the suction pressure. Calculate or determine the desired compression ratio based on the requirements of your application. It will depend on factors such as the downstream processes, system pressure requirements, and safety considerations.
3. Gas Flow Rate: Determine the required gas flow rate or volume flow rate for your application. This will help you choose a compressor with the appropriate capacity to handle the desired flow rate efficiently. Consider factors such as peak demand, variations in gas flow, and any potential future expansion or changes in production requirements.
4. Operating Conditions: Assess the operating conditions of your application, including the temperature and pressure range within which the compressor will operate. Consider the ambient conditions, fluctuations in temperature and pressure, and any specific requirements for the gas mixture being compressed. Ensure the selected compressor can handle the anticipated operating conditions without compromising performance or safety.
5. Gas Properties: Consider the properties of the gas mixture, such as its molecular weight, density, viscosity, and compressibility. These properties can impact the compressor's efficiency, power requirements, and potential challenges like gas slippage or heat transfer. Ensure the selected compressor is compatible with the gas properties and can operate optimally.
6. Compressor Type: Evaluate the different types of mixed gas compressors available, such as reciprocating, rotary screw, centrifugal, or others, based on your specific requirements. Consider factors like efficiency, capacity, maintenance requirements, initial costs, and suitability for handling your gas mixture. Each compressor type has its advantages and limitations, so choose the type that aligns with your needs.
7. Ancillary Equipment and Safety: Consider any additional equipment or components required for the compressor system, such as filters, separators, coolers, or safety devices. These components can impact the overall system performance, gas quality, and safety. Ensure the selected compressor can be integrated effectively with the necessary ancillary equipment.
8. Energy Efficiency: Energy efficiency is an essential consideration. Look for compressors with high efficiency ratings to minimize energy consumption and operating costs. Consider features like variable speed drives, energy recovery systems, or control mechanisms that can optimize energy usage based on demand.
9. Manufacturer and Support: Research reputable compressor manufacturers with a track record of quality, reliability, and after-sales support. Consider factors like warranty, availability of spare parts, technical support, and maintenance services. Choosing a reliable manufacturer ensures long-term support and reduces the risk of operational disruptions.
10. Budget and Cost Analysis: Evaluate the initial investment cost, operating costs, and lifecycle costs associated with the compressor. Consider factors such as purchase price, installation costs, energy consumption, maintenance requirements, and potential downtime. Perform a cost analysis to determine the most cost-effective option that meets your requirements.

Some corresponding mixed gas compressor parameters based on different application scenarios:
1. Industrial Process Applications:
- Gas Composition: Understand the composition of the mixed gas, including its individual components and concentrations.
- Compression Ratio: Determine the required compression ratio based on downstream processes, system pressure requirements, and safety considerations.
- Gas Flow Rate: Calculate the required gas flow rate or volume flow rate based on the process demands and variations in gas flow.
- Operating Conditions: Consider the temperature and pressure range within which the compressor will operate, accounting for ambient conditions and fluctuations.
- Gas Properties: Evaluate properties like molecular weight, density, viscosity, and compressibility to select a compressor that can handle the gas mixture effectively.
- Compressor Type: Choose a compressor type based on the gas mixture properties, required flow rate, and compression ratio. Reciprocating or rotary screw compressors are commonly used in industrial processes.
2. Oil and Gas Applications:
- Gas Composition: Analyze the composition of the mixed gas, including hydrocarbon components, impurities, and potential corrosive elements.
- Compression Ratio: Determine the compression ratio required for transporting or processing the gas in the oil and gas operations.
- Gas Flow Rate: Calculate the gas flow rate based on the production volume and transportation requirements.
- Operating Conditions: Consider the temperature and pressure conditions specific to the oil and gas application, including variations and extreme conditions.
- Gas Properties: Assess properties like molecular weight, density, viscosity, and potential for gas condensation to select a compressor suitable for oil and gas environments.
- Compressor Type: Centrifugal compressors are often used in oil and gas applications due to their high capacity and ability to handle a wide range of gas compositions.
3. Petrochemical and Refining Applications:
- Gas Composition: Understand the composition of the mixed gas, including hydrocarbons, gases, and potential contaminants found in petrochemical and refining processes.
- Compression Ratio: Determine the compression ratio based on the desired product specifications, downstream processes, and system requirements.
- Gas Flow Rate: Calculate the gas flow rate based on the production capacity and refining process needs.
- Operating Conditions: Consider the specific temperature and pressure conditions within the petrochemical or refining facility, accounting for variations and potential corrosive elements.
- Gas Properties: Evaluate properties like molecular weight, density, viscosity, and potential for gas impurities to select a compressor suitable for petrochemical and refining applications.
- Compressor Type: Depending on the requirements, both centrifugal and reciprocating compressors can be used in petrochemical and refining processes.
4. Gas Transmission and Distribution:
- Gas Composition: Analyze the composition of the mixed gas, including natural gas components and potential contaminants.
- Compression Ratio: Determine the compression ratio required for efficient gas transmission and distribution, considering pipeline specifications and pressure requirements.
- Gas Flow Rate: Calculate the gas flow rate based on the transmission or distribution capacity and demand.
- Operating Conditions: Consider the specific temperature and pressure conditions along the gas transmission or distribution pipeline, accounting for variations and potential gas quality issues.
- Gas Properties: Evaluate properties like molecular weight, density, viscosity, and potential for gas contaminants to select a compressor suitable for gas transmission and distribution.
- Compressor Type: Centrifugal compressors are commonly used in gas transmission and distribution due to their high capacity and efficiency.
5. Biogas and Landfill Gas Applications:
- Gas Composition: Analyze the composition of the biogas or landfill gas, including methane (CH4), carbon dioxide (CO2), and potential impurities like hydrogen sulfide (H2S).
- Compression Ratio: Determine the compression ratio based on the desired gas quality, pipeline specifications, and utilization requirements.
- Gas Flow Rate: Calculate the gas flow rate based on the biogas or landfill gas production capacity and demand.
- Operating Conditions: Consider the specific temperature and pressure conditions within the biogas or landfill gas facility, accounting for variations and potential impurities.
- Gas Properties: Evaluate properties like methane content, density, corrosiveness, impurity levels, and potential for gas contaminants to select a compressor suitable for biogas and landfill gas applications.
- Compressor Type: Rotary screw or reciprocating compressors are often used for biogas and landfill gas applications, considering the gas composition and required compression ratio.
6. Air Separation and Gas Liquefaction:
- Gas Composition: Analyze the composition of the mixed gas, especially if it involves air separation processes to extract specific gases.
- Compression Ratio: Determine the compression ratio required for gas liquefaction or separation processes, considering the desired purity levels and downstream requirements.
- Gas Flow Rate: Calculate the gas flow rate based on the production capacity and specific gas separation or liquefaction needs.
- Operating Conditions: Consider the specific temperature and pressure conditions within the air separation or gas liquefaction facility, accounting for variations and potential contaminants.
- Gas Properties: Evaluate properties like molecular weight, density, boiling points, and potential for gas impurities to select a compressor suitable for air separation and gas liquefaction applications.
- Compressor Type: Centrifugal compressors are often used in air separation and gas liquefaction processes due to their high capacity and ability to handle varying gas compositions.
7. Natural Gas Storage:
- Gas Composition: Analyze the composition of the natural gas, including methane (CH4), hydrocarbons, and potential contaminants.
- Compression Ratio: Determine the compression ratio required for efficient natural gas storage and withdrawal, considering storage pressure requirements and pipeline specifications.
- Gas Flow Rate: Calculate the gas flow rate based on the storage capacity and withdrawal needs.
- Operating Conditions: Consider the specific temperature and pressure conditions within the natural gas storage facility, accounting for variations and potential gas quality issues.
- Gas Properties: Evaluate properties like methane content, density, viscosity, impurity levels, and potential for gas contaminants to select a compressor suitable for natural gas storage applications.
- Compressor Type: Reciprocating compressors are commonly used in natural gas storage facilities due to their ability to handle varying pressures and flow rates.
8. Hydrogen Refueling Stations:
- Gas Composition: Analyze the composition of the mixed gas, specifically focusing on hydrogen (H2) content and potential impurities.
- Compression Ratio: Determine the compression ratio required for efficient hydrogen refueling, considering the desired storage pressure and fueling requirements.
- Gas Flow Rate: Calculate the gas flow rate based on the refueling station capacity and demand.
- Operating Conditions: Consider the specific temperature and pressure conditions within the hydrogen refueling station, accounting for variations and potential impurities.
- Gas Properties: Evaluate properties like hydrogen content, density, moisture levels, and potential for impurities to select a compressor suitable for hydrogen refueling applications.
- Compressor Type: Diaphragm compressors or reciprocating compressors are commonly used in hydrogen refueling stations due to their ability to handle high-pressure gases.
9. Gas Recovery and Recycling:
- Gas Composition: Analyze the composition of the mixed gas, focusing on the target gas to be recovered and potential impurities.
- Compression Ratio: Determine the compression ratio required for efficient gas recovery and recycling, considering the desired purity levels and downstream processes.
- Gas Flow Rate: Calculate the gas flow rate based on the gas recovery capacity and recycling needs.
- Operating Conditions: Consider the specific temperature and pressure conditions within the gas recovery and recycling system, accounting for variations and potential contaminants.
- Gas Properties: Evaluate properties like molecular weight, density, impurity levels, and potential for gas contaminants to select a compressor suitable for gas recovery and recycling applications.
- Compressor Type: Depending on the specific requirements, rotary screw compressors, reciprocating compressors, or centrifugal compressors may be suitable for gas recovery and recycling processes.
10. Research and Laboratory Applications:
- Gas Composition: Understand the composition of the mixed gas used in the research or laboratory setting, including specific gases and their concentrations.
- Compression Ratio: Determine the compression ratio required for the research or laboratory processes, considering the desired experimental conditions and gas handling requirements.
- Gas Flow Rate: Calculate the gas flow rate based on the experimental setup and process needs.
- Operating Conditions: Consider the specific temperature and pressure conditions within the research or laboratory facility, accounting for variations and experimental requirements.
- Gas Properties: Evaluate properties like molecular weight, density, viscosity, and potential for gas impurities to select a compressor suitable for research and laboratory applications.
- Compressor Type: Depending on the specific requirements, oil-free compressors, scroll compressors, or other specialized compressors may be suitable for research and laboratory applications.
Remember that these are general examples, and each application may have unique considerations. It's important to consult with experts or compressor manufacturers who specialize in the specific field or industry to determine the optimal parameters and compressor type for your particular application scenario.
【不见星空汉服完整播放】注册登录

Hi! Welcome back.
How are you doing?
Let s talk! We’ll provide the perfect solution for you!

Since its establishment, ASC Compressor has focused on comprehensive solutions for Oilfield industry, CNG/LNG industry, Environmental protection, and Industrial compression. It has excellent quality in designing, researching, producing and manufacturing.
- Quick Link > Home > Products > Applications > News > About > Contact
-
Contact Us
- E-Mail: [email protected]
- Tel: +8618098536798/+86(0)5633698699
- Fax: +86(0)5633698699
-
Address:
No. 17 Xingye Road, Economic Development Zone, Xuanzhou District, Xuancheng City, Anhui Province, China