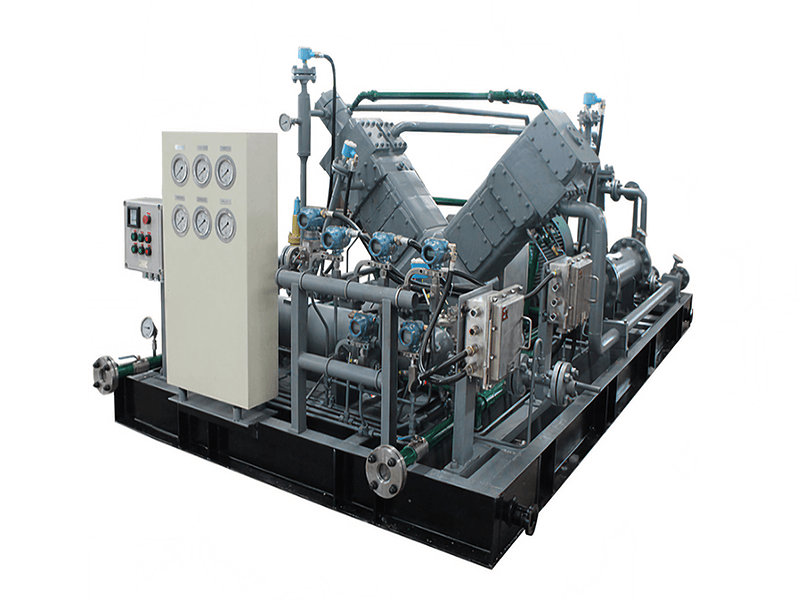
Choosing a natural gas compressor requires careful consideration of several factors to ensure optimal performance and efficiency. Here are some steps to guide you in the selection process:
1. Determine the Application: Identify the specific application for which you need the compressor. This could include gas production, transmission, distribution, or a specific industrial process. Understanding the requirements and demands of the application will help determine the appropriate compressor type and specifications.
2. Gas Volume and Pressure Requirements: Determine the required flow rate (volume) and the desired discharge pressure for the gas. This information will help determine the capacity and pressure rating of the compressor needed to meet your requirements.
3. Gas Composition: Analyze the composition of the natural gas, including the presence of contaminants, corrosive elements, and hydrocarbon dew point. This information is crucial for selecting materials and components that can withstand the gas composition without degradation or failure.
4. Efficiency Considerations: Evaluate the desired efficiency level for the compressor. Higher efficiency leads to reduced energy consumption and operational costs. Consider the expected duty cycle, operating conditions, and energy requirements to select a compressor that can optimize efficiency for your specific application.
5. Compressor Type: Familiarize yourself with different compressor types, such as reciprocating, centrifugal, screw, or rotary vane compressors. Each type has its own advantages, limitations, and operating characteristics. Choose the type that best suits your application requirements, taking into account factors such as flow rate, pressure ratio, and gas composition.
6. Space and Installation Considerations: Evaluate the available space for installation, including considerations for foundation requirements, ventilation, and noise limitations. Ensure that the selected compressor can be accommodated within the available space without compromising safety or operational requirements.

7. Maintenance and Serviceability: Consider the maintenance requirements and serviceability of the compressor. Assess factors such as maintenance intervals, accessibility of components, availability of spare parts, and the manufacturer's support services. A reliable maintenance plan and access to necessary resources will help ensure long-term performance and minimize downtime.
8. Safety and Environmental Considerations: Take into account safety features and compliance with environmental regulations. Consider features such as pressure relief valves, emergency shutdown systems, and emission control devices to ensure safe operation and adherence to environmental standards.
9. Consult with Experts: Seek guidance from qualified engineers, compressor manufacturers, and industry experts. They can provide valuable insights, help evaluate your specific requirements, and recommend suitable compressor options based on their experience and expertise.
10. Cost Analysis: Consider the initial purchase cost, operational costs (such as energy consumption and maintenance), and the expected lifecycle of the compressor. Conduct a comprehensive cost analysis to determine the most cost-effective solution that meets your application requirements.
By carefully considering these factors and seeking expert advice, you can make an informed decision when selecting a natural gas compressor that best suits your needs, ensuring reliable and efficient gas compression operations.
Parameters of Natural Gas Compressors
Natural gas compressors are essential components of gas processing and transportation systems. They are used to increase the pressure of natural gas, allowing for efficient and reliable movement through pipelines. Compressors play a crucial role in various industries, including natural gas production, transmission, and distribution.
1. Flow Rate: The flow rate refers to the volume of gas compressed by the compressor per unit of time, typically measured in cubic feet per minute (CFM) or cubic meters per hour (m³/h). It indicates the capacity of the compressor to handle gas volumes.
2. Pressure Ratio: The pressure ratio is the ratio of the discharge pressure to the suction pressure. It quantifies the level of pressure increase achieved by the compressor. Higher pressure ratios require more energy and often involve multiple stages of compression.
3. Horsepower (HP): Horsepower is a measure of the power output of a compressor. It indicates the energy required to drive the compressor and is often used to specify the size and capacity of the equipment.
4. Efficiency: Compressor efficiency refers to the effectiveness with which a compressor converts input energy into useful work. It is typically expressed as a percentage and represents the ratio of the actual work done (compressing the gas) to the energy input.
5. Discharge Temperature: The discharge temperature is the temperature of the gas leaving the compressor. Compressing natural gas generates heat, and controlling the discharge temperature is crucial to prevent equipment damage and ensure safe operation.
6. Compressor Type: There are various types of natural gas compressors, including reciprocating compressors, centrifugal compressors, screw compressors, and rotary vane compressors. Each type has its own operating characteristics, advantages, and limitations.
7. Maintenance Intervals: Compressors require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance and reliability. Maintenance intervals indicate the frequency of inspections, lubrication, filter changes, and other maintenance tasks that need to be performed on the compressor.
8. Noise Level: Noise level is an important consideration, especially in residential or noise-sensitive areas. Compressors can produce significant noise during operation, and minimizing noise emissions may be a requirement to comply with local regulations.
9. Safety Features: Natural gas compressors often incorporate various safety features, such as pressure relief valves, temperature sensors, and emergency shutdown systems. These features help prevent equipment failures, protect against overpressure or overheating, and ensure safe operation.
10. Suction Pressure: The suction pressure is the initial pressure of the gas entering the compressor. It is crucial to know the suction pressure to determine the appropriate compressor type and size for the desired pressure ratio.
11. Discharge Pressure: The discharge pressure is the pressure at which the compressed gas is expelled from the compressor. It depends on the requirements of the downstream processes or pipeline system and determines the necessary pressure ratio of the compressor.
12. Compression Stage: Compressors can have single-stage or multi-stage configurations. Single-stage compressors compress the gas in a single step, while multi-stage compressors have two or more stages to achieve higher pressure ratios. Multi-stage compressors are often used for high-pressure gas transportation.
13. Cooling Method: Compressing natural gas generates heat, and cooling is required to maintain safe operating temperatures. Compressors can use various cooling methods, including air-cooling, water-cooling, or a combination of both. The choice of cooling method depends on factors such as ambient conditions, gas composition, and operational requirements.
14. Lubrication: Compressors require lubrication to reduce friction, minimize wear and tear, and ensure smooth operation. The lubrication method can vary based on the compressor type, and proper lubricant selection is crucial to avoid compatibility issues and maintain optimal performance.
15. Control Systems: Compressors often incorporate sophisticated control systems to regulate operation and optimize performance. These systems may include automation, monitoring of parameters such as pressure and temperature, fault detection, and remote operation capabilities.
16. Environmental Considerations: Compressors should comply with environmental regulations and standards. This includes considerations for emissions control, such as the use of emission control devices, monitoring systems, and adherence to air quality requirements.
17. Installation Requirements: Compressors have specific installation requirements related to foundation design, ventilation, noise mitigation, and safety considerations. Proper installation is essential to ensure efficient operation, minimize vibrations, and maintain a safe working environment.
18. Gas Composition: The composition of natural gas can vary, and it influences the selection and design of compressors. Factors such as the presence of contaminants, corrosive components, or high hydrocarbon dew point can impact the choice of materials, compressor type, and maintenance requirements.
It's important to work closely with qualified engineers, natural gas compressor manufacturers, and industry experts to determine the appropriate parameters and specifications for natural gas compressors based on the specific application and operational conditions.