【比思论坛官网最新消息】最新入口
-

CNG Standard Station Compressor Types And Price Ranges
May 29, 2024 -

Characteristics of requirements for butadiene compressors in different industries
Jun 27, 2024 -

Types And Prices Of Wellhead Gas Compressors
Apr 11, 2024 -

Some Things To Pay Attention To When Purchasing Casing Gas Compressors
Apr 11, 2024 -

What is casing gas?
May 01, 2024 -

Methods and steps for natural gas recovery
Jun 14, 2024
比思论坛官网最新消息【乾坤易变】Apr 25, 2024
by:Anhui Shengnuo Compressor Manufacturing Co.,Ltd
Follow Us:
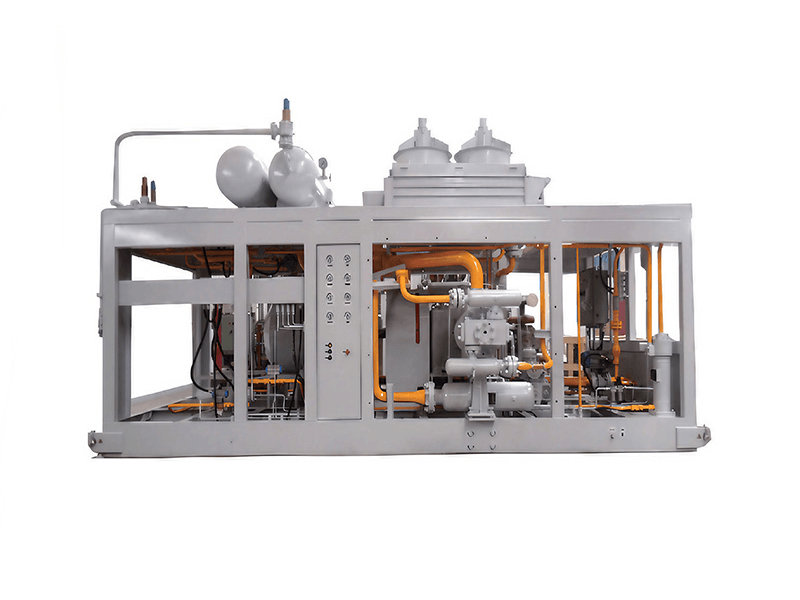
Casing gas compressors play an important role in natural gas production and processing operations. Here are some of the key functions of casing gas compressors:
1. Pressure Maintenance: Casing gas compressors are used to maintain the pressure in the annular space between the production casing and the wellbore. By compressing the gas in this space, the compressor helps to prevent fluid influx from surrounding formations, ensuring the integrity and stability of the well.
2. Gas Lift: Casing gas compressors are commonly used in gas lift operations to enhance oil or gas production from wells. The compressor injects compressed gas into the annular space, creating pressure that lifts the hydrocarbons from the wellbore to the surface. This technique helps increase production rates and prolong the productive life of the well.
3. Gas Gathering: Casing gas compressors are utilized in gas gathering systems to collect and compress the natural gas produced from multiple wells in a field. The compressor helps maintain the pressure and flow of the gas as it is transported through pipelines to processing facilities or transmission networks.
4. Vapor Recovery: Casing gas compressors are employed in vapor recovery units (VRUs) to capture and compress hydrocarbon vapors emitted during the storage and handling of volatile liquids, such as crude oil, gasoline, or natural gas liquids. The compressor helps recover these vapors for further processing or re-injection, reducing emissions and minimizing product losses.

5. Gas Sealing: Casing gas compressors also serve as gas seal systems in certain applications. They are used to maintain a higher pressure inside the equipment or system, creating a gas barrier that prevents the ingress of external contaminants or gases.
6. Well Testing: Casing gas compressors are utilized during well testing operations to maintain a controlled pressure and flow rate during the testing process. The compressor helps regulate the pressure in the wellbore and surface equipment, enabling accurate measurements of reservoir properties and fluid flow characteristics.
7. Gas Injection: Casing gas compressors can be used for gas injection operations, where compressed gas is injected into underground reservoirs to enhance oil recovery or to store natural gas. The compressor pressurizes the injected gas, enabling it to displace and mobilize the hydrocarbons within the reservoir.
8. Gas Dehydration: Casing gas compressors can be utilized in gas dehydration systems to remove moisture or water vapor from the natural gas stream. The compressor helps pressurize the gas, facilitating the separation of water through condensation or absorption processes, resulting in drier gas suitable for transportation or further processing.
9. Gas Compression for Storage: Casing gas compressors are employed in natural gas storage facilities to compress the gas before it is stored underground in depleted reservoirs or caverns. The compressor ensures that the gas is compressed to the desired pressure for efficient storage and subsequent withdrawal when demand arises.
10. Gas Transmission: Casing gas compressors are used in natural gas transmission pipelines to maintain the pressure and flow of the gas over long distances. The compressor stations along the pipeline network compress the gas periodically to compensate for pressure losses, ensuring the gas reaches its destination reliably and efficiently.
11. Gas Conditioning: Casing gas compressors can be involved in gas conditioning processes, where the composition and properties of the natural gas are adjusted to meet specific requirements. The compressor plays a role in compressing the gas and facilitating subsequent treatments such as removing impurities, adjusting temperature or pressure, or separating valuable components.
12. Offshore Gas Compression: Casing gas compressors are employed in offshore production facilities to compress and transport the associated gas or gas lift gas from subsea wells to the surface processing facilities or transportation systems. These compressors are designed to withstand the unique challenges of offshore environments and ensure the efficient recovery and utilization of the gas resources.
13. Enhanced Oil Recovery (EOR): Casing gas compressors can be utilized in enhanced oil recovery methods such as gas flooding or miscible gas injection. The compressor pressurizes the injected gas, enabling it to sweep through the reservoir and displace the oil, facilitating its recovery and maximizing production.
14. Gas Control and Regulation: Casing gas compressors are used in gas control and regulation systems to maintain specific pressure levels in the gas distribution networks. The compressor helps ensure a consistent and reliable gas supply to end-users by controlling and adjusting the gas pressure according to demand fluctuations and system requirements.
15. Gas Reinjection: Casing gas compressors are used in gas reinjection operations, where compressed gas is injected back into the reservoir to maintain reservoir pressure and improve hydrocarbon recovery. The compressor pressurizes the gas to the desired injection pressure, allowing it to be reintroduced into the formation.
16. Gas Blowdown: Casing gas compressors can be employed in gas blowdown operations, where gas is released from pressurized storage tanks or pipelines to reduce excess pressure. The compressor helps control and regulate the rate at which the gas is released, ensuring safe and efficient blowdown operations.
17. Gas Blanketing: Casing gas compressors are used for gas blanketing applications, where a layer of inert gas is maintained on top of stored liquids or sensitive equipment to prevent oxidation, contamination, or undesired reactions. The compressor supplies the inert gas and helps maintain the required pressure in the blanket.
18. Gas Injection for Chemical Processes: Casing gas compressors can be utilized for gas injection in chemical processes, such as oxidation or hydrogenation reactions. The compressor supplies the necessary compressed gas, allowing it to be introduced into the process for desired chemical transformations.
19. Pressure Boosting: Casing gas compressors are employed to boost the pressure of natural gas to meet specific operational requirements. This can include increasing the pressure of the gas for downstream processes, transportation, or to overcome pressure drops in the system.
20. Flare Gas Recovery: Casing gas compressors can be used in flare gas recovery systems, where they capture and compress the gas that would otherwise be flared or wasted. This recovered gas can then be utilized for various purposes, such as fuel for on-site operations or injected back into the production system.
21. Gas Fueling Stations: Casing gas compressors are utilized in natural gas fueling stations for vehicles powered by compressed natural gas (CNG) or liquefied natural gas (LNG). The compressor pressurizes the gas to the required level for efficient refueling of vehicles.
22. Mobile Gas Compression: Casing gas compressors can be mounted on mobile units, such as trailers or trucks, for temporary or remote gas compression needs. These mobile compressors offer flexibility and can be transported to different locations as required.
23. Gas Processing: Casing gas compressors are used in gas processing facilities to compress and transport the natural gas through various stages of the processing system. They help maintain the pressure and flow of the gas as it undergoes treatment processes such as separation, purification, and fractionation.
24. Gas Injection for Reservoir Pressure Maintenance: Casing gas compressors can be utilized for reservoir pressure maintenance in depleted or low-pressure gas reservoirs. The compressor injects compressed gas into the reservoir to maintain or increase the pressure, enhancing the productivity and recovery of hydrocarbons.
25. Gas Export: Casing gas compressors play a crucial role in gas export operations, where natural gas is compressed for transportation via pipelines or liquefied natural gas (LNG) terminals. The compressor ensures that the gas is compressed to the required pressure for efficient and cost-effective transportation to distant markets.
26. Gas Storage Cycling: Casing gas compressors are used in gas storage facilities that involve cyclic operations, such as seasonal storage or peak shaving. The compressor facilitates the compression and injection of gas during the storage phase and the subsequent withdrawal and decompression during the extraction phase.
27. Gas Pressure Equalization: Casing gas compressors can be employed to equalize the pressure between different sections or zones within a gas system. By compressing gas from a high-pressure zone and injecting it into a low-pressure zone, the compressor helps maintain a balanced pressure profile in the system.
28. Emergency Backup: Casing gas compressors can serve as emergency backup units in the event of primary compressor failure or system disruptions. They provide redundancy and ensure continuity of operations by stepping in to maintain the required gas pressure and flow during unforeseen circumstances.
29. Gas Conditioning for Fuel Gas Systems: Casing gas compressors are used to condition the natural gas used as fuel in various industrial processes or power generation systems. The compressor helps compress and prepare the gas by removing impurities, adjusting pressure and temperature, and ensuring its suitability for combustion or energy conversion.
30. Gas Pressure Testing: Casing gas compressors are involved in gas pressure testing operations, where the integrity and strength of gas pipelines, storage tanks, or equipment are evaluated. The compressor pressurizes the system to the desired test pressure, allowing for the detection of leaks or structural weaknesses.
These are some functions of casing gas compressors in various applications within the oil and gas industry, energy sector, and related fields. The specific utilization of casing gas compressors depends on factors such as project requirements, system design, operational goals, and industry standards.
【比思论坛官网最新消息】注册登录

Hi! Welcome back.
How are you doing?
Let s talk! We’ll provide the perfect solution for you!

Since its establishment, ASC Compressor has focused on comprehensive solutions for Oilfield industry, CNG/LNG industry, Environmental protection, and Industrial compression. It has excellent quality in designing, researching, producing and manufacturing.
- Quick Link > Home > Products > Applications > News > About > Contact
-
Contact Us
- E-Mail: [email protected]
- Tel: +8618098536798/+86(0)5633698699
- Fax: +86(0)5633698699
-
Address:
No. 17 Xingye Road, Economic Development Zone, Xuanzhou District, Xuancheng City, Anhui Province, China