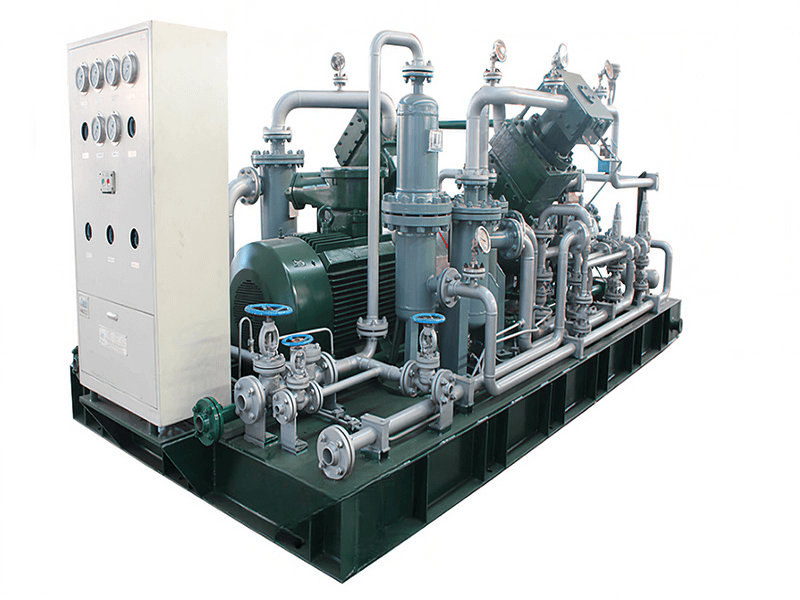
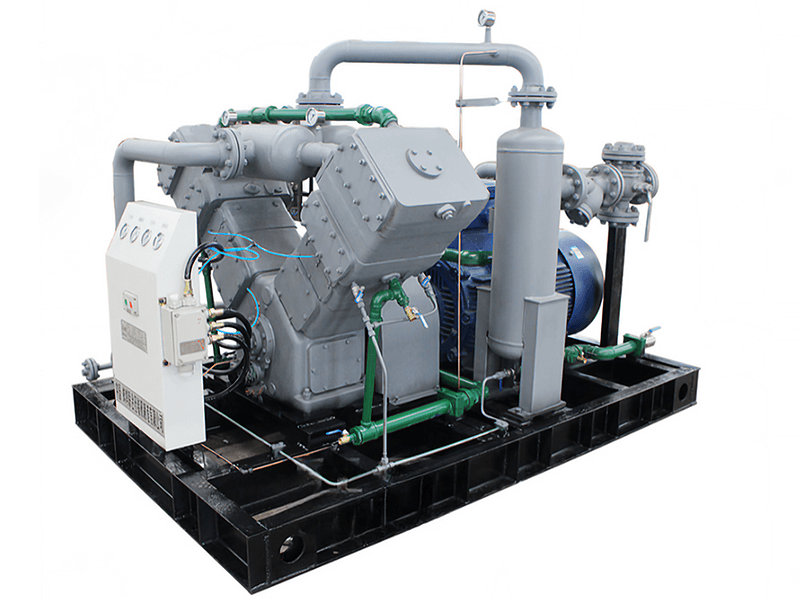
Compressing ammonia gas involves using a ammonia compressor to increase the pressure of the gas. Here are the general steps involved in compressing ammonia gas:
1. Safety Precautions: Before handling and compressing ammonia gas, it is essential to follow proper safety protocols. This includes wearing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), ensuring proper ventilation in the area, and working in accordance with safety guidelines and regulations.
2. Compressor Selection: Select a compressor suitable for compressing ammonia gas. Consider factors such as the required pressure range, flow rate, and the properties of ammonia gas. Ensure that the compressor is compatible with handling ammonia and has appropriate seals and materials that can withstand the corrosive nature of ammonia.
3. Preparing the System: Ensure that the compression system is clean, free from contaminants, and properly maintained. Verify that the compressor and associated piping and equipment are in good working condition.
4. Inlet Preparation: Connect the inlet pipe or line to the system where the ammonia gas will enter the compressor. Ensure that the inlet pipe is properly sized and has appropriate filters or separators to remove any impurities or moisture that may be present in the gas.

5. Compression Process: Start the compressor and adjust the operating parameters based on the desired compression ratio and pressure requirements. The compressor will draw in the ammonia gas from the inlet and compress it, increasing its pressure. The compressed gas is then discharged from the compressor.
6. Cooling and Heat Management: During compression, the ammonia gas may heat up due to the compression process. It is important to manage the heat generated and maintain appropriate temperatures to prevent overheating. This can be achieved through cooling systems, heat exchangers, or other temperature control methods.
7. Outlet and Discharge: Connect the outlet pipe or line to the compressed gas outlet of the compressor. Ensure that the outlet pipe is properly sized and designed to handle the high-pressure ammonia gas. The compressed gas can be directed to storage tanks, piping systems, or further processing units as required.
8. Monitoring and Control: Monitor the compression process closely, including pressure levels, temperature, and any other relevant parameters. Use appropriate instrumentation and control systems to ensure safe and efficient operation.
9. Safety Shutdown and Maintenance: Implement proper safety measures, including emergency shutdown procedures, in case of any abnormalities or emergencies. Regularly inspect and maintain the compressor and associated equipment to ensure continued safe and efficient operation.
It is important to note that compressing ammonia gas should only be carried out by trained professionals familiar with the handling and safety aspects of ammonia. Proper safety precautions and guidelines must be followed to prevent any accidents or hazards associated with working with ammonia.
Applications
Ammonia compression is utilized in various industries and applications. Here are some of the key areas where ammonia compression plays a crucial role:
1. Refrigeration and Air Conditioning: Ammonia compression is widely used in industrial refrigeration and air conditioning systems. Ammonia is an efficient refrigerant with excellent heat transfer properties, and compression is necessary to raise its pressure and temperature for heat exchange processes. Ammonia compression allows for the creation of cooling effects in refrigeration systems, enabling the storage and preservation of perishable goods and maintaining comfortable indoor temperatures.
2. Chemical Industry: Ammonia compression is essential in the chemical industry for various processes. Ammonia is a key ingredient in the production of fertilizers, such as ammonium nitrate and urea. Compression is required during the synthesis of ammonia through the Haber-Bosch process, where hydrogen and nitrogen react under high pressure and temperature. Ammonia compression also facilitates the transportation and storage of ammonia for further chemical reactions and applications.
3. Power Generation: Ammonia compression is utilized in power generation systems that utilize ammonia as a fuel or working fluid. Ammonia can be combusted in gas turbines or used in advanced power cycles, such as ammonia-water Rankine cycles, to generate electricity. Compression is necessary to pressurize the ammonia for efficient combustion or to raise its pressure for power conversion in turbines.
4. Hydrogen Production: Ammonia compression plays a role in the production of hydrogen through the process of ammonia decomposition. Ammonia can be decomposed into hydrogen and nitrogen using heat, and compression is required to separate and collect the hydrogen gas. Ammonia compression allows for the extraction and storage of hydrogen, which can be used for various applications, including fuel cells and industrial processes.
5. Chemical Storage and Transportation: Ammonia compression enables the storage and transportation of ammonia in its liquid or gaseous form. Ammonia is often stored and transported under high pressure to maintain its stability and prevent vaporization or leakage. Compressed ammonia is commonly transported in specialized containers, such as cylinders or tanks, to be utilized in various industrial processes and applications.
6. Water Treatment: Ammonia compression is utilized in water and wastewater treatment processes. Ammonia is commonly used in the form of ammonium hydroxide for pH adjustment, disinfection, and the removal of contaminants. Compression of ammonia allows for controlled dosing and distribution of ammonia in water treatment systems, ensuring effective treatment and maintaining desired water quality parameters.
7. Research and Development: Ammonia compression is crucial in research and development efforts focused on ammonia-based technologies and applications. Research institutions and laboratories often require compressed ammonia for experimental investigations, testing prototypes, and validating ammonia-based systems.
8. Food and Beverage Industry: Ammonia compression plays a role in the food and beverage industry for applications such as food processing, cold storage, and freezing. Ammonia is commonly used as a refrigerant in large-scale industrial refrigeration systems, and compression is necessary to maintain the desired temperature levels and support the preservation of food products.
9. Pharmaceuticals and Healthcare: Ammonia compression finds application in the pharmaceutical and healthcare sectors. Ammonia is used in various pharmaceutical processes, such as the production of medicines and drugs. Compression is employed to provide the necessary pressure for chemical reactions and separation processes during pharmaceutical manufacturing.
10. Environmental Applications: Ammonia compression is utilized in environmental applications, including air pollution control and wastewater treatment. In air pollution control, ammonia is used as a reagent for selective catalytic reduction (SCR) systems to reduce nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions from combustion processes. Compression ensures the proper delivery and mixing of ammonia with flue gases. In wastewater treatment, ammonia compression is employed for processes such as ammonia stripping and biological nutrient removal.
11. Energy Storage: Ammonia compression is being explored as a potential energy storage medium. Ammonia can be produced using renewable energy sources through the process of electrolysis, and the compressed ammonia can be stored and later converted back into electricity or heat when energy demand is high. Ammonia compression plays a crucial role in the storage and release of energy from ammonia-based storage systems.
12. Metal Heat Treatment: Ammonia compression is used in metal heat treatment processes, such as annealing, brazing, and case hardening. Ammonia dissociates into nitrogen and hydrogen at high temperatures, and compression is required to maintain the desired pressure for these heat treatment applications. Ammonia dissociation provides a controlled atmosphere conducive to specific metallurgical transformations.
13. Textile Industry: Ammonia compression is employed in the textile industry for applications such as dyeing and printing. Ammonia is used as a fixing agent for dyes, and compression ensures its efficient delivery and distribution for the dyeing processes.
14. Cleaning and Surface Treatment: Ammonia compression is utilized in cleaning and surface treatment applications. Ammonia-based solutions are used for cleaning surfaces, removing stains, and degreasing. Compression allows for the controlled application of ammonia solutions in various cleaning processes.
15. Research and Testing Facilities: Ammonia compression is vital in research and testing facilities that focus on ammonia-related technologies, materials, and processes. Compressed ammonia is utilized for experimental studies, prototype testing, and performance evaluations of ammonia-based systems and components.
These are some of the key applications of ammonia compression in various industries. Ammonia's versatility as a refrigerant, chemical precursor, energy carrier, and water treatment chemical makes compression an essential process for its efficient use and application in diverse sectors.