Coalbed methane (CBM), also known as coal seam gas or coal mine methane, is a type of natural gas that is found within coal deposits. It is formed during the geological process of coalification, where organic matter in plant debris transforms into coal over millions of years.
Here are some key characteristics and features of coalbed methane:
1. Origin: Coalbed methane is generated through the thermal maturation of organic material within coal seams. As the coal forms, methane gas is trapped within the coal matrix and the cleats (natural fractures) of the coal.
2. Composition: Coalbed methane is predominantly composed of methane (CH4), typically with smaller amounts of other hydrocarbons such as ethane (C2H6), propane (C3H8), and trace amounts of higher hydrocarbons. It can also contain impurities like nitrogen (N2), carbon dioxide (CO2), and water vapor.
3. Extraction: Coalbed methane is extracted by drilling wells into coal seams. Unlike conventional natural gas reservoirs, the extraction process involves removing water from the coal seam to lower the pressure, allowing the gas to desorb from the coal and flow to the wellbore. The water produced alongside the gas is often referred to as "produced water" and requires appropriate management.
4. Environmental Considerations: Coalbed methane extraction can have both positive and negative environmental impacts. On the positive side, capturing and utilizing coalbed methane can reduce emissions of methane, a potent greenhouse gas, into the atmosphere. However, extraction operations must be carefully managed to prevent potential groundwater contamination and the release of methane during the extraction process.
5. Uses: Coalbed methane has similar applications to conventional natural gas. It can be used for heating, electricity generation, industrial processes, and as a feedstock for the production of chemicals and fuels. In some cases, coalbed methane is utilized on-site at coal mines to provide energy for mining operations.
6. Economic Significance: Coalbed methane has gained economic importance due to its potential as a valuable energy resource. In regions with extensive coal deposits, coalbed methane extraction has become a significant industry, contributing to energy production and economic development.
It's worth noting that the extraction of coalbed methane requires specialized techniques and considerations due to the unique properties of coal seams. The management of water and the design of well completions are crucial factors in the successful extraction of coalbed methane.
Overall, coalbed methane represents a significant unconventional natural gas resource that can contribute to energy supplies while requiring careful management to mitigate environmental impacts.
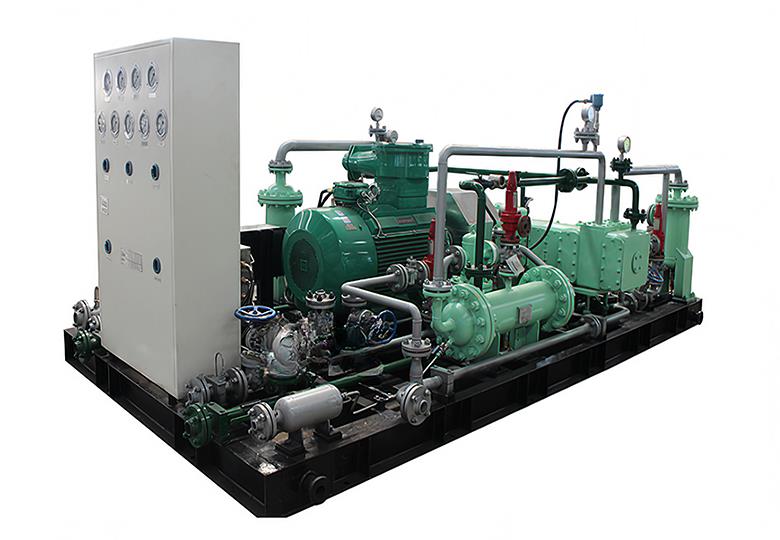
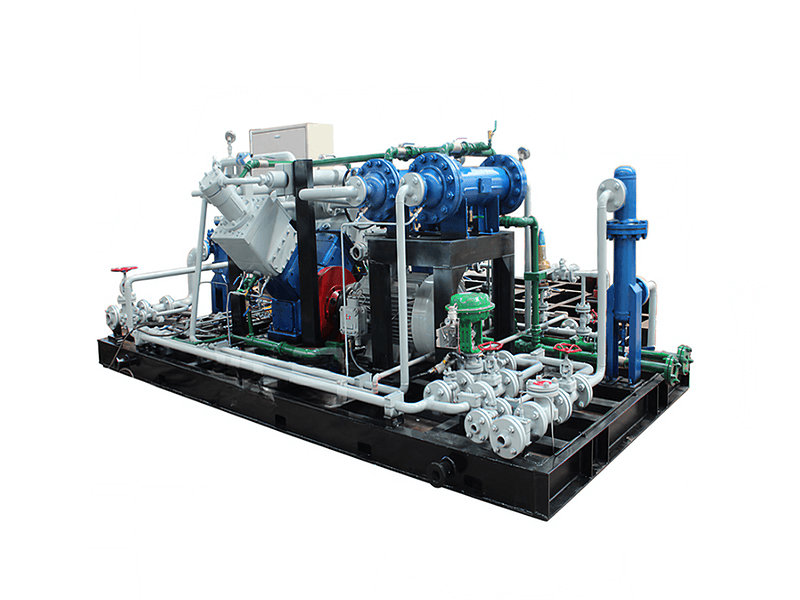
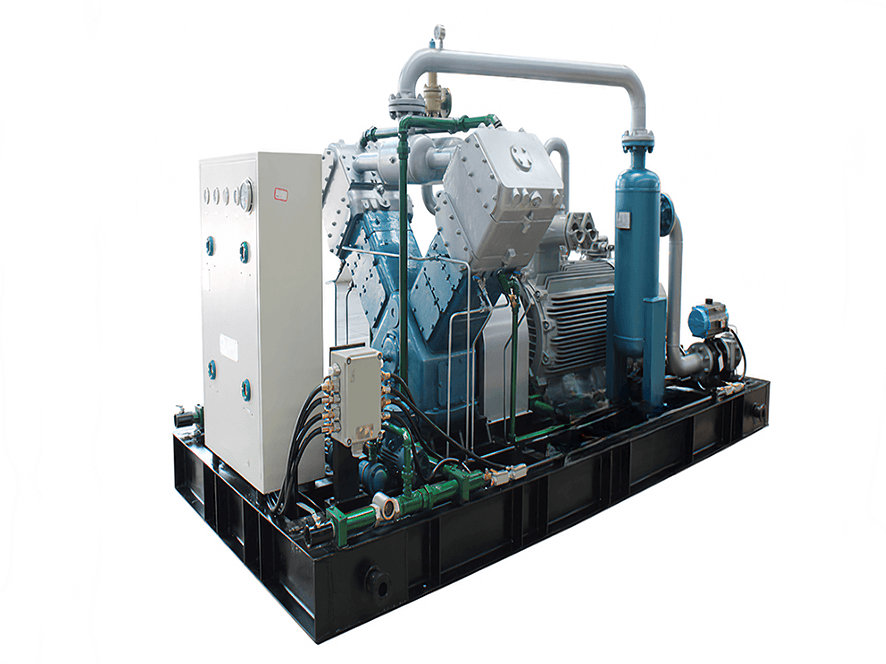
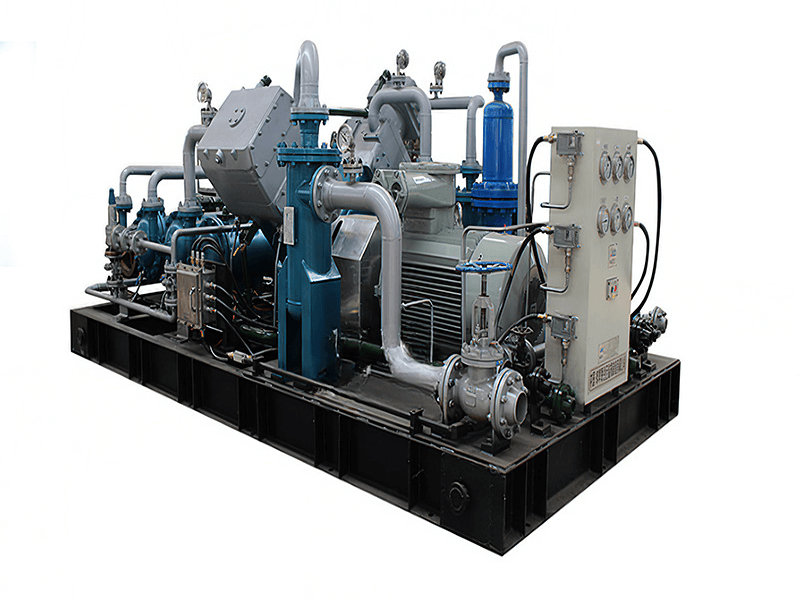
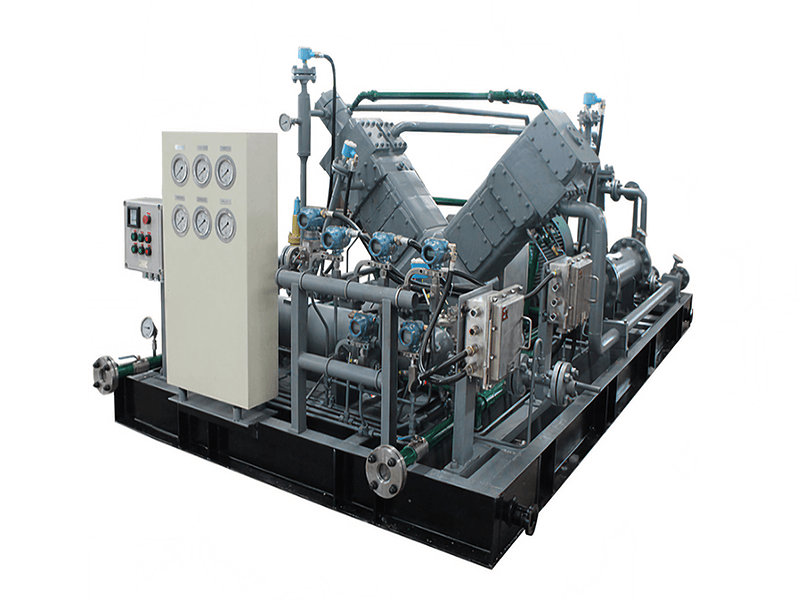
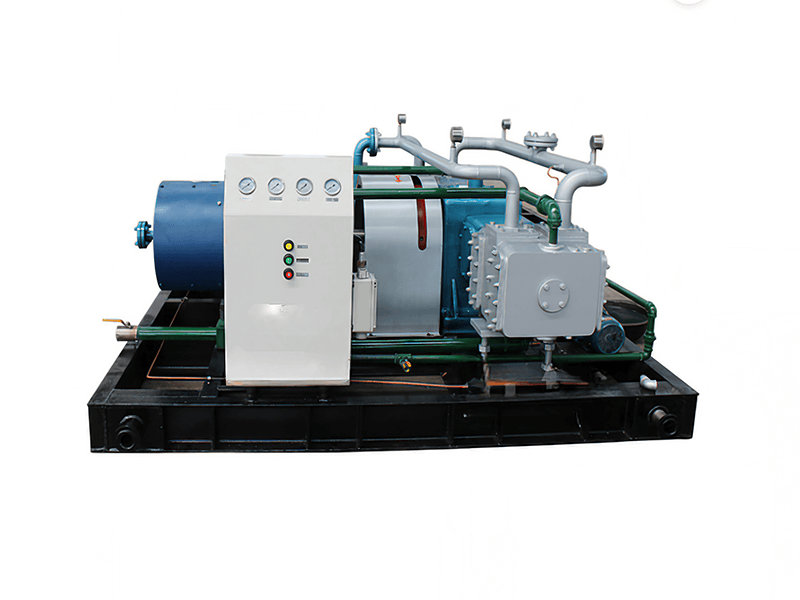
A Coalbed Methane (CBM) recovery compressor is a specific type of compressor used in the extraction and production of coalbed methane gas. It is designed to handle the unique characteristics and requirements associated with the compression of methane gas from coal seams.
Here are some key features and considerations related to CBM recovery compressors:
1. Gas Compression: CBM recovery compressors are specifically designed to compress the extracted methane gas from coal seams. The compressors increase the pressure of the gas to facilitate its transportation, storage, or further processing.
2. Gas Composition: CBM recovery compressors must be compatible with the composition of coalbed methane gas. They are designed to handle the typical composition of methane (CH4) along with potential impurities such as nitrogen (N2), carbon dioxide (CO2), and water vapor. The compressor must be constructed using materials that are resistant to these gases and any corrosive elements present in the gas stream.
3. Efficiency and Performance: CBM recovery compressors are engineered to operate efficiently while maintaining high performance. They are designed to handle the specific flow rates and pressure requirements associated with coalbed methane extraction operations. The compressors typically have features such as multiple stages of compression to achieve the desired pressure increase.
4. Safety: Safety is a crucial consideration in CBM recovery compressors due to the potentially hazardous nature of the extracted methane gas. The compressors are equipped with safety features, such as pressure relief valves, emergency shutdown systems, and gas detection systems, to prevent overpressure situations, mitigate risks, and protect personnel and equipment.
5. Environmental Considerations: CBM recovery compressors play a role in mitigating greenhouse gas emissions by capturing and compressing methane, a potent greenhouse gas, for utilization or storage. Properly designed and maintained compressors help reduce fugitive methane emissions during the extraction and production process.
6. Site-Specific Requirements: CBM recovery compressors are often customized to meet the specific requirements of the coalbed methane extraction site. Factors such as gas flow rates, pressure conditions, site location, environmental regulations, and project economics influence the selection and configuration of the compressors.
It is essential to consult with compressor manufacturers and industry experts to select the appropriate CBM recovery compressor that meets the specific needs and conditions of the coalbed methane extraction operation. Proper installation, maintenance, and adherence to safety guidelines are crucial for the reliable and efficient operation of CBM recovery compressors.