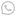
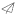
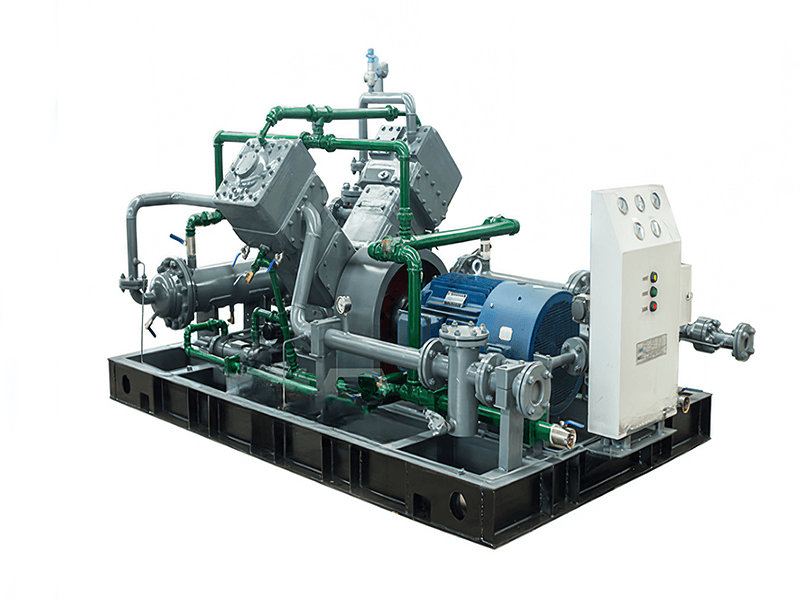
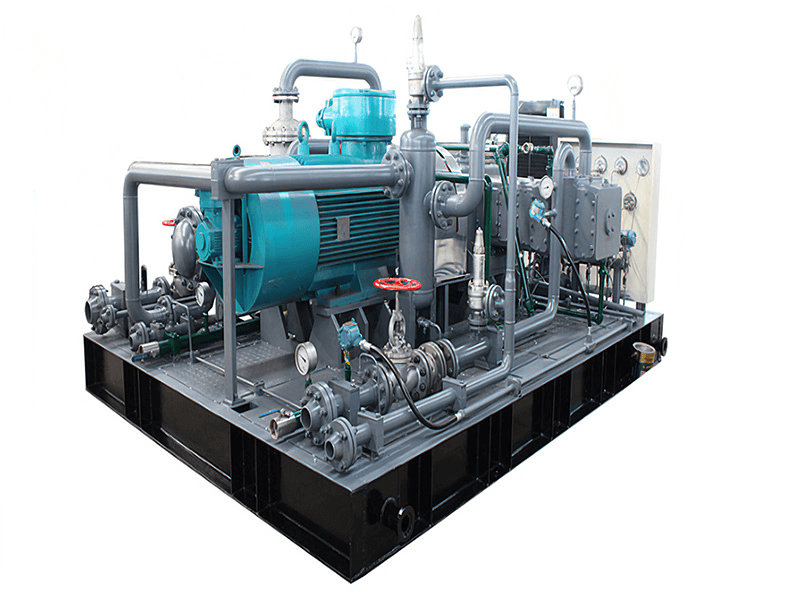
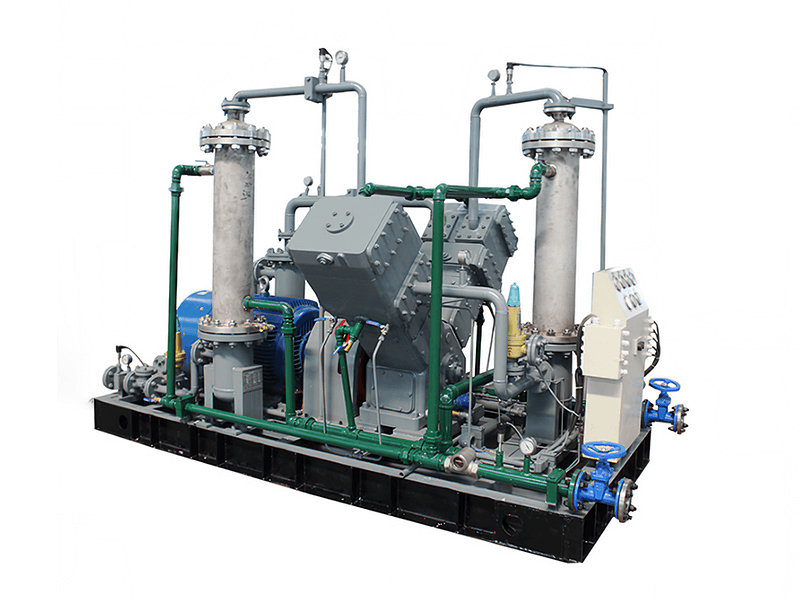
Hydrogen Compressor
Date: May 09, 2024
By: Anhui Shengnuo Compressor Manufacturing Co.,Ltd
A hydrogen compressor is a type of compressor specifically designed to handle hydrogen gas. It is used to compress hydrogen gas from a lower pressure to a higher pressure, making it suitable for various applications such as hydrogen fueling stations, hydrogen storage systems, and industrial processes.
Hydrogen compressors are essential in the hydrogen economy as they play a crucial role in the production, storage, and distribution of hydrogen. They enable the efficient transportation of hydrogen gas and facilitate its utilization in fuel cells and other hydrogen-powered devices.
Functions of hydrogen compressor
Hydrogen compressors serve several important functions in various applications related to the production, storage, and distribution of hydrogen. Here are some key functions of hydrogen compressors:
1. Compression of Hydrogen Gas: The primary function of a hydrogen compressor is to increase the pressure of hydrogen gas. Hydrogen is often produced or stored at lower pressures, and compressors are used to raise the pressure to the desired level for efficient transportation, storage, or utilization.
2. Hydrogen Fueling: In hydrogen fueling stations for fuel cell vehicles, hydrogen compressors play a crucial role. They compress hydrogen gas to the required pressure for refueling vehicles, ensuring efficient and rapid fueling.
3. Hydrogen Storage: Hydrogen compressors are used in hydrogen storage systems to pressurize and store hydrogen gas. By compressing the gas, its volume decreases, allowing for more hydrogen to be stored in a given space. Compressors help increase the storage capacity and enable efficient utilization of storage infrastructure.
4. Hydrogen Distribution: Compressed hydrogen gas needs to be transported from production facilities to end-use locations such as fueling stations or industrial facilities. Hydrogen compressors facilitate the distribution process by compressing the gas for efficient and cost-effective transportation through pipelines or high-pressure cylinders.
5. Industrial Processes: Hydrogen is widely used in various industrial processes, such as oil refining, chemical manufacturing, and semiconductor production. Hydrogen compressors are employed to supply compressed hydrogen gas to these processes, ensuring a reliable and consistent source of hydrogen.
6. Hydrogen Liquefaction: Hydrogen compressors are utilized in hydrogen liquefaction plants where hydrogen gas is cooled and condensed into a liquid state. Compressors play a crucial role in raising the pressure of gaseous hydrogen before it enters the liquefaction process.
7. Hydrogen Energy Systems: Hydrogen compressors are integral components of hydrogen energy systems, including fuel cell systems and hydrogen-powered turbines. They deliver compressed hydrogen gas to these systems, enabling efficient and reliable power generation.
8. Pressure Regulation: Hydrogen compressors are often equipped with pressure regulation mechanisms. They can control and maintain a consistent output pressure, ensuring that the compressed hydrogen gas meets the specific requirements of the application or system it is being supplied to.
9. Gas Purification: In some cases, hydrogen compressors are integrated with gas purification systems. These systems remove impurities, moisture, and other contaminants from the hydrogen gas before it is compressed. This ensures the delivery of high-purity hydrogen gas for applications where purity is critical, such as fuel cells and certain industrial processes.
10. System Efficiency: Hydrogen compressors contribute to overall system efficiency by minimizing energy losses and optimizing the compression process. Compressors with advanced designs and control systems can achieve higher compression efficiencies, reducing energy consumption and operational costs.
11. Safety Measures: Hydrogen compressors incorporate safety features to handle the specific characteristics of hydrogen gas. They may include mechanisms to prevent hydrogen leakage, explosion-proof designs, and monitoring systems for temperature, pressure, and other parameters to ensure safe operation.
12. System Integration: Hydrogen compressors are often integrated into larger hydrogen systems, working in conjunction with other components such as hydrogen generators, storage tanks, and dispensing equipment. They provide the necessary pressure and flow required for seamless integration and operation of the overall system.
13. Customization and Adaptability: Hydrogen compressors can be customized to meet specific requirements of different applications. They can be designed to handle various pressure ranges, flow rates, and gas compositions, ensuring compatibility with the unique needs of different industries and processes.
Hydrogen compressors are critical components in the infrastructure supporting the utilization of hydrogen as an energy carrier. They enable the effective and reliable compression, storage, distribution, and utilization of hydrogen gas, contributing to the advancement of hydrogen-based technologies and the transition to a clean energy future.
Application industries of hydrogen compressors
Hydrogen compressors find applications in various industries where the compression, storage, and distribution of hydrogen gas are required. Some of the key industries that utilize hydrogen compressors include:
1. Hydrogen Fueling Stations: Hydrogen fueling stations use compressors to compress hydrogen gas for refueling fuel cell vehicles (FCVs) and other hydrogen-powered vehicles. Compressors play a crucial role in providing the necessary pressure to fill the onboard hydrogen storage tanks of these vehicles.
2. Energy Storage: Hydrogen is being explored as an energy storage medium, particularly for renewable energy sources. Compressors are used in hydrogen energy storage systems to compress and store hydrogen gas during periods of excess renewable energy generation. The stored hydrogen can later be used for power generation through fuel cells or hydrogen combustion.
3. Chemical Industry: The chemical industry utilizes hydrogen in various processes, such as ammonia production, methanol synthesis, and hydrogenation reactions. Hydrogen compressors are employed to compress and deliver hydrogen gas to these industrial processes, ensuring the required pressure and flow rates.
4. Oil Refining: Hydrogen is an essential component in oil refining processes, such as hydrocracking and hydrotreating. Hydrogen compressors are used to compress and supply hydrogen gas to these refining processes, aiding in the conversion of heavy hydrocarbons into lighter and more valuable products.
5. Power Generation: Hydrogen can be used as a fuel in gas turbines and combined-cycle power plants. Compressors are utilized to compress hydrogen gas before its combustion, ensuring efficient power generation.
6. Electronics Manufacturing: Hydrogen is used in the electronics industry for wafer fabrication, particularly in the production of semiconductors. Hydrogen compressors are employed to supply high-purity hydrogen gas required for these manufacturing processes.
7. Aerospace and Aviation: The aerospace industry utilizes hydrogen as a propellant for rockets and as a fuel for aircraft. Hydrogen compressors play a vital role in compressing hydrogen gas for propulsion systems, enabling efficient and high-thrust operation.
8. Research and Development: Hydrogen compressors are utilized in research and development activities related to hydrogen storage, fuel cell testing, and hydrogen-related technologies. They provide the necessary pressure and flow control for experimental setups and testing equipment.
9. Metal Heat Treatment: Hydrogen is often used in heat treatment processes for metals, such as annealing, brazing, and sintering. Hydrogen compressors are employed to supply compressed hydrogen gas to create the desired atmosphere and conditions for these heat treatment processes.
10. Food and Beverage Manufacturing: Hydrogen is used in the food and beverage industry for various applications, including hydrogenation of edible oils, carbonation of beverages, and modified atmosphere packaging. Hydrogen compressors are utilized to provide compressed hydrogen gas for these processes.
11. Glass Industry: Hydrogen is used in the glass industry for glass melting and annealing processes. Hydrogen compressors are employed to supply compressed hydrogen gas as a fuel for glass furnaces, aiding in efficient and controlled glass production.
12. Environmental Testing: Hydrogen compressors are used in environmental testing laboratories for applications such as leak testing, gas chromatography, and environmental simulation chambers. They provide compressed hydrogen gas for these testing and analysis procedures.
13. Research and Development: Hydrogen compressors are utilized in various research and development activities related to hydrogen storage, fuel cell development, hydrogen production, and other hydrogen-related technologies. They play a crucial role in providing the necessary pressure and flow control in laboratory-scale setups and experimental systems.
14. Medical and Pharmaceutical Applications: Hydrogen finds applications in the medical and pharmaceutical industries, such as hydrogenation reactions in pharmaceutical synthesis and hydrogen-based therapies. Hydrogen compressors are used to supply compressed hydrogen gas for these processes and applications.
15. Chemical Analysis and Laboratories: Hydrogen compressors are employed in chemical analysis laboratories, such as gas chromatography, mass spectrometry, and other analytical techniques. They provide compressed hydrogen gas as a carrier or fuel gas for accurate and reliable chemical analysis.
These examples highlight the diverse range of industries and applications where hydrogen compressors are utilized. As hydrogen continues to gain prominence as a clean and versatile energy carrier, the demand for hydrogen compressors is expected to increase across multiple sectors, driving technological advancements and innovation in compressor design and performance.
Types of hydrogen compressors
There are different types of hydrogen compressors available, including reciprocating compressors, diaphragm compressors, and centrifugal compressors. Each type has its own advantages and is suited for specific applications based on factors such as required pressure ratios, flow rates, and system characteristics.
1. Reciprocating Compressors: Reciprocating compressors use pistons driven by a crankshaft to compress hydrogen gas. They are widely used in hydrogen fueling stations, industrial processes, and hydrogen storage systems. Reciprocating compressors offer high efficiency, can handle varying flow rates, and are suitable for both low and high-pressure applications.
2. Diaphragm Compressors: Diaphragm compressors use flexible diaphragms to compress hydrogen gas. They are often chosen for applications that require high purity and leak-tight compression. Diaphragm compressors are suitable for compressing hydrogen gas to moderate pressures and are commonly used in industries such as chemical processing, semiconductor manufacturing, and hydrogen fuel cell systems.
3. Centrifugal Compressors: Centrifugal compressors utilize rotating impellers to accelerate and compress hydrogen gas. They are known for their high flow rates and are suitable for large-scale hydrogen compression applications. Centrifugal compressors are commonly used in hydrogen liquefaction plants, hydrogen production facilities, and large-scale industrial processes.
4. Screw Compressors: Screw compressors use rotating screws to compress hydrogen gas. They are efficient and can handle a wide range of flow rates. Screw compressors are often used in hydrogen production, storage, and distribution systems, as well as in industries such as oil refining and petrochemicals.
5. Scroll Compressors: Scroll compressors use interlocking scrolls to compress hydrogen gas. They are compact, have fewer moving parts, and are known for their quiet operation. Scroll compressors find applications in small-scale hydrogen fueling stations, residential hydrogen energy systems, and portable hydrogen generators.
Each type of hydrogen compressor has its advantages and is suitable for different pressure ranges and flow rates. It is important to consider factors such as efficiency, reliability, safety features, maintenance requirements, and compatibility with hydrogen gas when selecting the appropriate type of hydrogen compressor for a specific application.
Components of hydrogen compressor
Hydrogen compressors consist of several key components that work together to facilitate the compression of hydrogen gas. While the specific design and components may vary depending on the type and manufacturer of the compressor, here are some common components found in hydrogen compressors:
1. Compressor Housing: The compressor housing encloses the internal components of the compressor, providing structural support and protection. It is typically made of sturdy materials that can withstand the pressures and forces involved in the compression process.
2. Compression Chamber: The compression chamber is where the hydrogen gas is compressed. It is designed to withstand the high pressures generated during compression and may incorporate features such as valves, ports, and inlet/outlet connections for the flow of hydrogen gas.
3. Compression Mechanism: The compression mechanism is the core component responsible for compressing the hydrogen gas. It varies depending on the type of compressor but can include components such as pistons, diaphragms, impellers, screws, or scrolls. The compression mechanism converts mechanical energy into pressure, reducing the volume of the hydrogen gas.
4. Motor or Drive System: Hydrogen compressors are driven by motors or drive systems that provide the necessary power to operate the compression mechanism. The motor may be electric or powered by another energy source, depending on the specific application and compressor type.
5. Cooling System: Compressing hydrogen gas generates heat, and a cooling system is often incorporated to dissipate this heat. It may include components such as heat exchangers, cooling fins, or cooling jackets to maintain optimal operating temperatures and prevent overheating.
6. Lubrication System: Some types of hydrogen compressors require lubrication to reduce friction and ensure smooth operation. The lubrication system may include oil reservoirs, pumps, filters, and distribution channels to deliver lubricant to moving parts within the compressor.
7. Valves: Valves control the flow of hydrogen gas into and out of the compression chamber. They ensure proper timing and direction of gas flow during the compression process. Common types of valves used in hydrogen compressors include intake valves, discharge valves, and pressure relief valves.
8. Instrumentation and Controls: Hydrogen compressors are equipped with instrumentation and control systems for monitoring and regulating various parameters. This may include pressure sensors, temperature sensors, flow meters, control valves, and control panels. These components enable precise control of the compression process and ensure safe and efficient operation.
9. Safety Features: Hydrogen compressors incorporate safety features to mitigate potential hazards associated with hydrogen gas. These features can include explosion-proof enclosures, pressure relief systems, gas leak detection systems, and emergency shutdown mechanisms.
10. Maintenance and Service Access: Hydrogen compressors are designed to allow easy access for maintenance, inspection, and service. They may include features such as removable panels, inspection ports, and access points for routine maintenance and repair.
It's important to note that the specific components and their configurations can vary based on the type, size, and design of the hydrogen compressor. Manufacturers may incorporate additional features and components specific to their compressor models to enhance performance, efficiency, and safety.
Maintenance of hydrogen compressor
Proper maintenance is crucial for ensuring the optimal performance, reliability, and longevity of hydrogen compressors. Here are some key aspects of hydrogen compressor maintenance:
1. Regular Inspection: Conduct regular inspections of the compressor to identify any signs of wear, damage, or leaks. Inspect components such as seals, valves, fittings, and connections for any abnormalities. Check for oil or coolant leaks and ensure proper lubrication where applicable.
2. Lubrication: If the hydrogen compressor requires lubrication, follow the manufacturer's guidelines for lubricant selection and change intervals. Monitor lubricant levels and quality, and perform regular lubricant analysis to ensure it is clean and functioning properly.
3. Filter Replacement: Replace filters, such as air filters or oil filters, as recommended by the manufacturer. Clean or replace filters that become clogged or restricted to maintain proper airflow and filtration.
4. Tighten Connections: Periodically check and tighten all connections, including bolts, nuts, and fittings. Loose connections can lead to leaks or compromised performance.
5. Cooling System Maintenance: If the hydrogen compressor has a cooling system, ensure that it is clean and free from debris or blockages. Regularly inspect cooling fins, heat exchangers, or other cooling components to maintain efficient heat dissipation.
6. Pressure Relief System Testing: Test the pressure relief system of the compressor to ensure it operates correctly and safely. This involves checking the functionality of pressure relief valves and verifying that they open at the specified pressure thresholds.
7. Monitoring and Control Systems: Regularly inspect and calibrate monitoring and control systems, including pressure sensors, temperature sensors, and control panels. Ensure that alarms, shutdown mechanisms, and safety features are functioning properly.
8. Vibration Analysis: Monitor and analyze vibrations produced by the compressor to identify any abnormal or excessive vibration levels. Excessive vibration can indicate mechanical issues that require attention.
9. Training and Operator Awareness: Provide proper training to operators and maintenance personnel on the operation, maintenance, and safety protocols specific to the hydrogen compressor. Ensure they understand the maintenance procedures and know how to identify and address potential issues.
10. Manufacturer Guidelines: Follow the manufacturer's recommended maintenance schedule, procedures, and guidelines specific to the hydrogen compressor model. Adhering to these guidelines helps ensure compliance with warranty requirements and best practices.
11. Service and Repair: If maintenance tasks require specialized knowledge or expertise, consult qualified technicians or service providers who are experienced with hydrogen compressors. They can perform more in-depth inspections, repairs, or overhauls as needed.
Remember to prioritize safety when conducting maintenance activities on hydrogen compressors. Follow proper lockout/tagout procedures, use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), and work in accordance with applicable safety regulations and guidelines.
By implementing a comprehensive maintenance program, you can enhance the performance, reliability, and safety of hydrogen compressors, minimizing downtime and optimizing their lifespan.
Price of hydrogen compressor
The price of a hydrogen compressor can vary significantly depending on various factors such as the compressor type, capacity, design, brand, and additional features. The prices can range from several thousand dollars for small, low-capacity compressors to hundreds of thousands or even millions of dollars for large, high-capacity industrial-grade compressors.
It's important to note that hydrogen compressors are specialized equipment designed for handling hydrogen gas, which requires specific materials, safety considerations, and technical specifications. These factors can contribute to the overall cost of the compressor.
Additionally, the rapidly evolving hydrogen industry and growing demand for hydrogen-related equipment may impact the pricing of hydrogen compressors. Factors such as market demand, availability of supply chains, and technological advancements can influence the pricing dynamics.
To get accurate and up-to-date pricing information for a specific hydrogen compressor, it is recommended to contact equipment manufacturers, distributors, or authorized dealers who can provide you with detailed pricing based on your specific requirements and application. They will be able to provide you with quotes and information tailored to your needs and assist you in selecting the most suitable compressor for your hydrogen-related operations.
Here are a few examples of hydrogen compressors along with their approximate price ranges. Please note that these prices are rough estimates and can vary based on the specific configurations and suppliers:
1. Small-Scale Hydrogen Compressors:
- Diaphragm Compressor: Prices can range from $5,000 to $20,000, depending on capacity and features.
- Reciprocating Piston Compressor: Prices can range from $10,000 to $50,000, depending on capacity and specifications.
- Scroll Compressor: Prices can range from $8,000 to $30,000, depending on capacity and features.
2. Medium-Scale Hydrogen Compressors:
- Reciprocating Piston Compressor: Prices can range from $50,000 to $200,000, depending on capacity, pressure requirements, and customization.
- Centrifugal Compressor: Prices can range from $100,000 to $500,000, depending on capacity, pressure requirements, and specifications.
3. Large-Scale Hydrogen Compressors:
- Reciprocating Piston Compressor: Prices can range from $200,000 to $1,000,000 or more, depending on capacity, pressure requirements, and customization.
- Centrifugal Compressor: Prices can range from $500,000 to several million dollars, depending on capacity, pressure requirements, and specifications.
It's important to note that these prices are approximate and may vary significantly depending on factors such as capacity, pressure range, materials of construction, control systems, and additional features required for specific applications. It is recommended to contact hydrogen compressor manufacturers, distributors, or authorized dealers to get accurate and up-to-date pricing information based on your specific needs and requirements.











 Jul 08, 2024
Jul 08, 2024